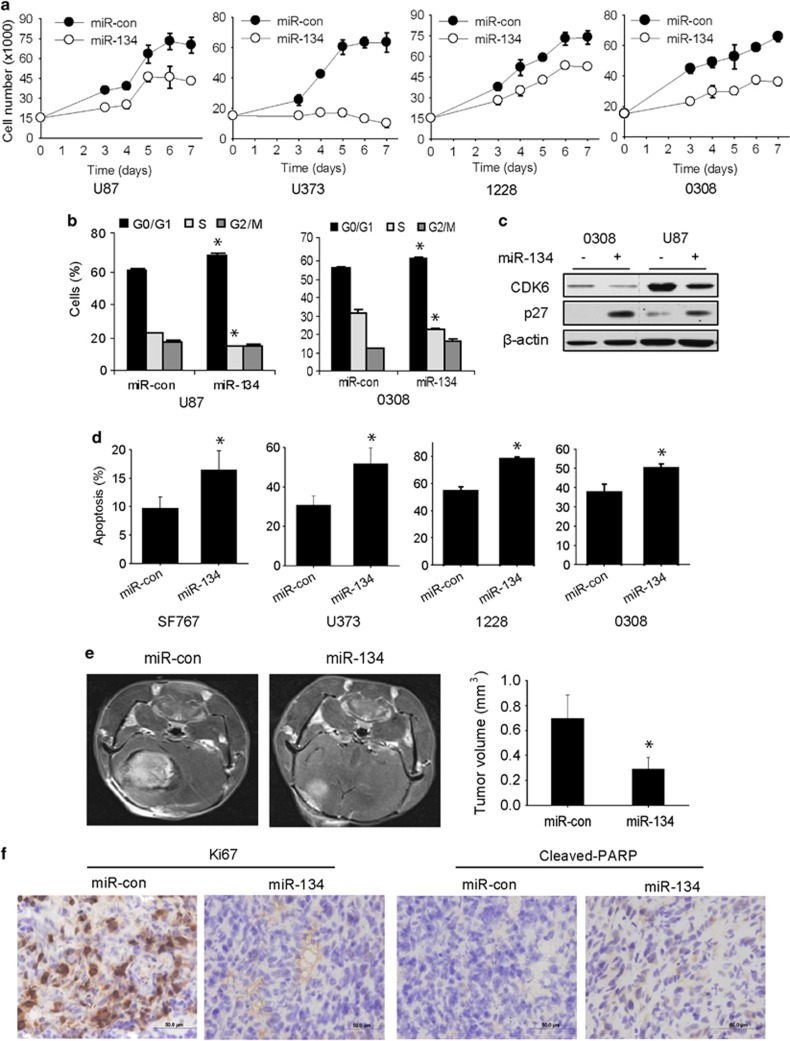
Figure 5.
miR-134 inhibits GBM cell and GSC proliferation, survival, and in vivo tumor growth. (a) Proliferation assay showing the inhibition of GBM cell and GSC proliferation by miR-134 transfection. (b) Flow-cytometric cell-cycle analysis showing cell-cycle arrest induced by miR-134 transfection in GBM cells and GSCs (left panel). (c) Immunoblot analysis of cell-cycle regulatory proteins in response to miR-134 transfection into GBM cells and GSCs (right panel). (d) AnnexinV-PE and 7-AAD flow-cytometric analysis of GBM cells and GSCs showing induction of apoptosis after miR-134 transfection. (e) GSC 1228 was transfected with pre-miR-134 or pre-miR-con and implanted into the brains of immunodeficient mice (n=6). After 4 weeks, the mice were subjected to MRI and tumor volume calculation. The results show that miR-134 inhibits in vivo GBM xenograft growth. (f) Immunohistochemical staining of xenograft sections from (e) for the proliferation marker Ki67 and the apoptotic marker cleaved-PARP showing significantly reduced Ki67 and increased cleaved-PARP in miR-134 overexpressing xenografts (section at × 400 magnification). *P<0.05