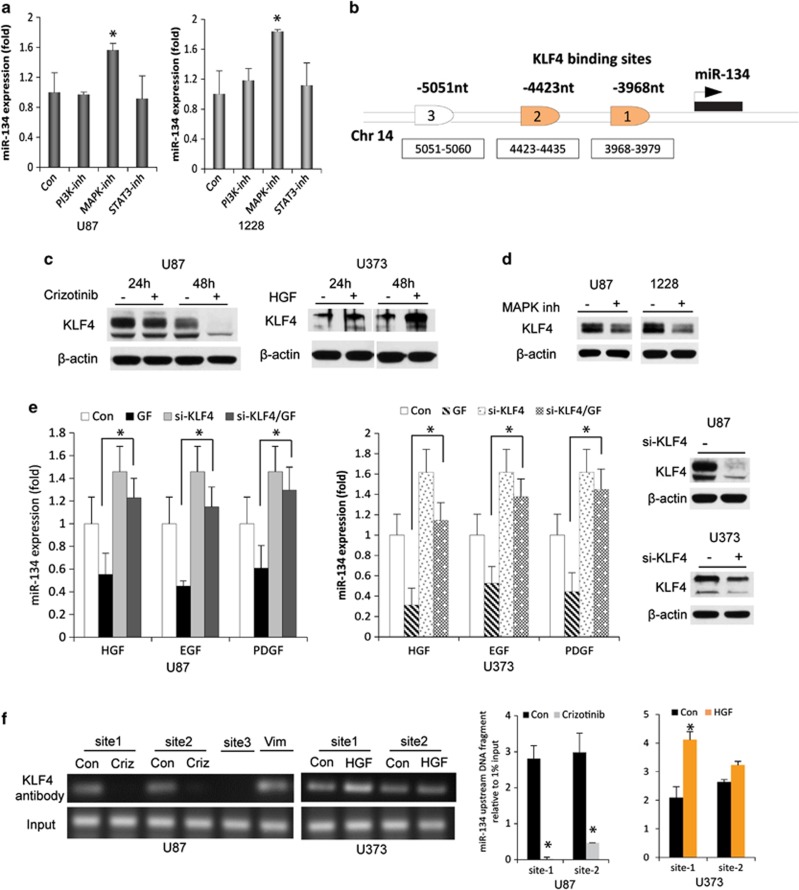
Figure 8.
RTKs regulate miR-134 expression via MAPK and KLF4. (a) GBM U87 and GSC 1228 cells were treated with inhibitors of PI3K, MAPK, and STAT3 and assessed for miR-134 expression by qRT-PCR. Only MAPK inhibition led to an upregulation of miR-134 expression in both cell lines. (b) KLF4 predicted binding sites in the putative miR-134 promoter. (c) Immunoblots showing the effect of MET inhibition and activation on KLF4 expression in GBM cells. (d) Immunoblots showing the downregulation of KLF4 expression after MAPK inhibition in GBM cells and GSCs. (e) Rescue experiments showing that siRNA-based KLF4 knockdown reverses the inhibitory effects on miR-134 expression of MET, EGFR, and PDGFR activations with their respective growth factor (GF) ligands in GBM cells (two left panels). Right panel shows immunoblots with KLF4 knockdown. (f) ChIP/qPCR showing the binding of KLF4 to two KLF4 binding sites (site 1 and site 2) in the putative miR-134 promoter in response to MET inhibition or activation with Crizotinib (criz) or HGF, respectively. Vimentin (Vim) was used as a positive control. Left panel shows ChIP/qPCR and right panel shows its quantification. *P<0.05