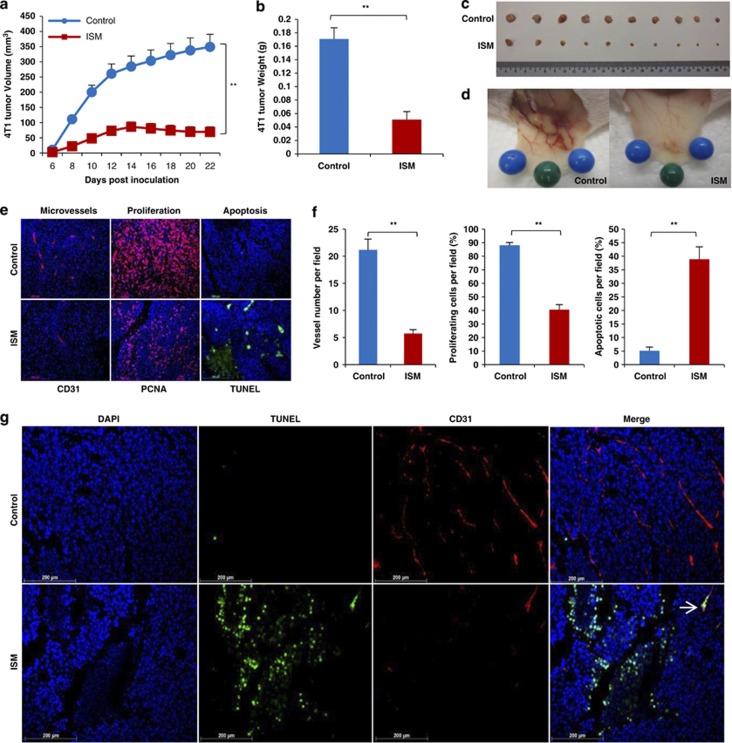
Figure 8.
Systemically delivered rISM suppresses 4T1 breast carcinoma growth in mice by inducing apoptosis of both cancer cells and cancer ECs. (a–d) ISM inhibits 4T1 breast carcinoma growth in mice when delivered systematically. (a) 4T1 tumor growth curve in mice. X-axis represents the days after inoculation of 1 × 106 tumor cells. Groups consisted of control mice receiving no treatment or 250 μg rISM through tail vein injection every other day from day 0 (date of inoculation) to 22. N=10. (b) Tumor weight at the end of the experiment (day 22). (c) Dissected tumors at the end of experiment. (d) rISM-treated tumors showed a reduced vascularization compared with untreated control. (e) rISM-suppressed tumor angiogenesis, proliferation and induced apoptosis in 4T1 tumor. Paraffin sections of 4T1 tumors from control and treated groups with rISM were probed for microvascular density (MVD), tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis through IF using anti-CD31, anti-PCNA and TUNEL staining, respectively. (f) Quantification of MVD, cell proliferation and apoptosis. Plots represent the mean of three fields per section, three sections per tumor and two tumors per group. **P<0.01. Error bars denote S.E.M. (g) ISM induces apoptosis of both cancer cells and cancer ECs in 4T1 breast carcinoma. Double IF using anti-CD31 (red) and TUNEL (green) is shown. Nuclei were counterstained by DAPI (blue). Representative photos are shown. Apoptotic EC is indicated by white arrow