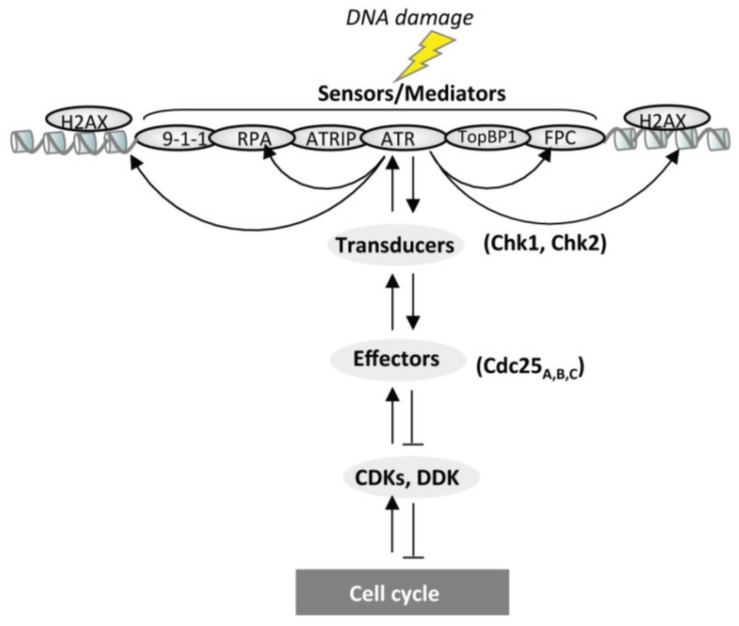
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the replication checkpoint pathway activated following DNA damage. DNA damage generated onto the DNA induces activation and/or relocalization of sensor and mediator proteins triggering a phosphorylation cascade (downwards arrows) that in turn activates soluble, as well as chromatin-bound, transducers and effector proteins resulting in cell cycle delay. Once the damage has been repaired signaling is inactivated by dephosphorylation (backwards arrows). FPC stands for Fork Protection Complex and includes Timeless, Claspin and Tipin proteins.