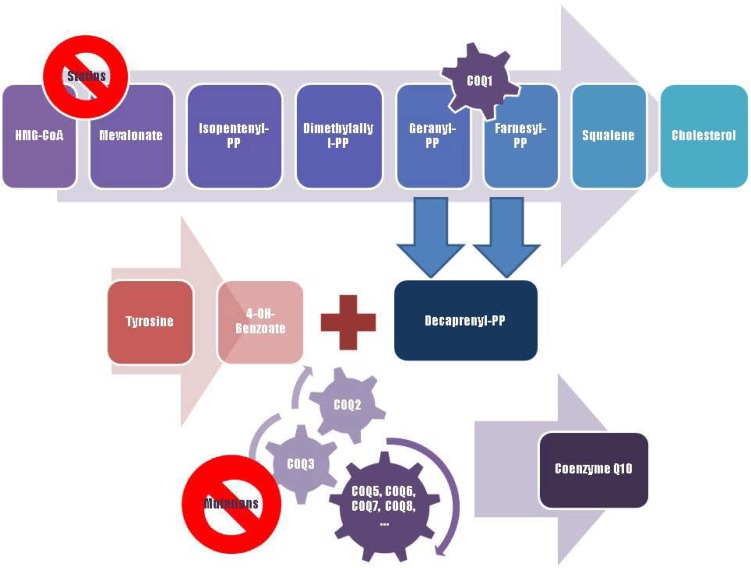
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of Coenzyme Q10 biosynthesis. The sequence of cellular reactions that leads to farnesyl-PP is the mevalonate pathway. Farnesyl-PP is the common substrate for the synthesis of cholesterol, dolichol, and Coenzyme Q10, as well as for prenylation of proteins. Coenzyme Q10 contains also a benzoate ring originating from tyrosine. 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors, or statins, block production of mevalonate, a critical intermediary in the cholesterol synthesis pathway. A hypothesized mechanism of statin myopathy involve mitochondrial dysfunction caused by reduced intramuscular coenzyme Q10. After 4-OH-benzoate and decaprenyl-PP are produced, at least seven enzymes (encoded by COQ2-8 genes) catalyze condensation, methylation, decarboxylation, and hydroxylation reactions needed to synthesize Coenzyme Q10. Abnormalities in any part of this metabolic cascade will cause primary CoQ10 deficiency. PP, pyrophosphate.