Figure 6.
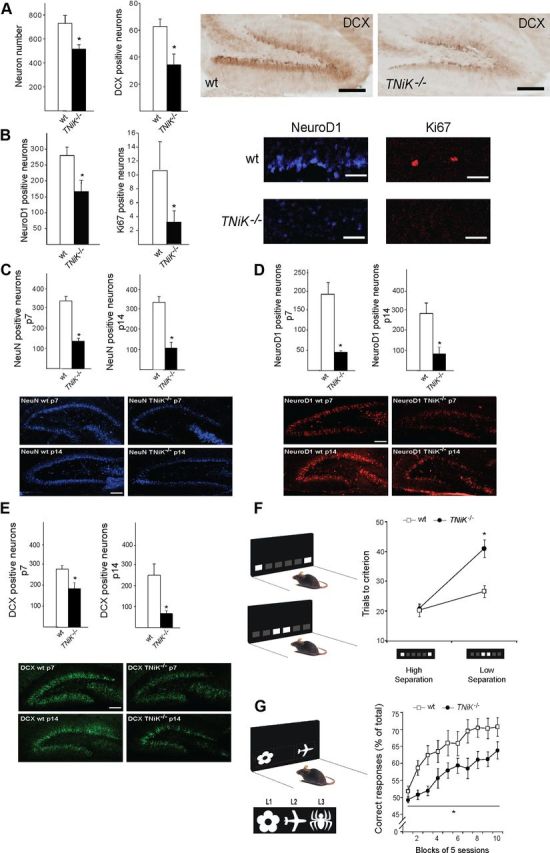
Impaired dentate gyrus neurogenesis and cognition in TNiK−/− mice. A, B, Histograms comparing dentate gyrus granule cell number and cells stained with markers relevant to neurogenesis (see text) in wt and TNiK−/− mice brain sections. Representative images of dentate gyrus cells in wt and TNiK−/− brain sections stained with markers for DCX (A), NeuroD1, and Ki67 (B). Scale bars: (in A) 200 and (in B) 60 μm. C–E, Hippocampus development in TNiK−/− mice. Number of NeuN-positive neurons at P7 (upper, left histogram) and P14 (lower, right histogram) in wt and TNiK−/− mice (C). Number of NeuroD1-positive neurons at P7 (upper, left histogram) and P14 (lower, right histogram) in wt and TNiK−/− mice (D). Number of DCX-positive neurons at P7 (upper, left histogram) and P14 (lower, right histogram) in wt and TNiK−/− mice (E). Scale bars: 100 μm. F, Pattern separation was assessed using a two-choice spatial discrimination task in the touchscreen-based operant system. Mice were trained to discriminate the correct spatial location between two illuminated squares, located in two of six possible locations. Pattern separation was tested by varying the distance between the choice locations, either situated far apart (high degree of separation; top) or close together (low degree of separation; bottom). TNiK−/− mice performed as well as wt mice when stimuli were separated by a high degree of separation; however, they showed a significant impairment (p < 0.05) in discrimination when the locations were in close proximity. As a control measure, analysis of response reaction times showed no significant differences between groups at either separation (high separation, wt = 5.0 ± 1.1 s, TNiK−/− = 5.2 ± 0.8s; low separation, wt = 4.9 ± 0.7 s, TNiK−/− = 5.0 ± 0.9 s). G, TNiK−/− mice show a deficit in object-location associative learning (significant effect of genotype, p < 0.05) where mice were tested for the ability to associate between three objects (flower, plane, and spider) with their correct spatial locations on the screen [left (L1), middle (L2), and right (L3), respectively].
