Figure 1.
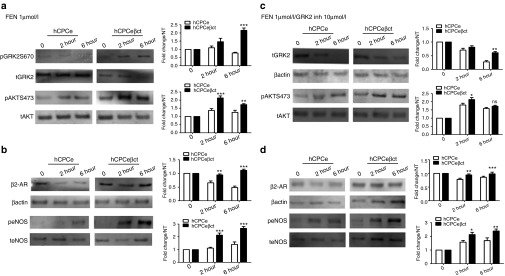
Characterization of molecular signaling in βARKct-engineered hCPCs. (a) Increased GRK2 phosphorylation in human cardiac progenitor cells overexpressing βARKct (hCPCeβct) after 2 and 6 hours of catecholamine stimulation compared with GFP expressing hCPCs (hCPCe; n = 3). Furthermore, increased AKT phosphorylation in hCPCeβct compared with hCPCe after catecholamine stimulation (n = 3). (b) Increased expression of β2-adrenergic receptor in hCPCeβct compared with hCPCe in response to catecholamine treatment. hCPCeβct maintain β2-adrenergic receptor even after 6 hours of catecholamine treatment compared with hCPCe (n = 3). Increased eNOS phosphorylation in hCPCeβct after catecholamine stimulation compared with hCPCe indicating activation of the prosurvival signaling (n = 3). (c) Decreased GRK2 levels in hCPCe compared with hCPCeβct after treatment with GRK2 inhibitor in the presence of catecholamine stimulation. Increased AKT phosphorylation in hCPCeβct compared with hCPCe after 2 hours of catecholamine stimulation in the presence of GRK2 inhibitor but the difference in not significant after 6 hours. (d) Increased β2-AR expression in hCPCeβct after 2 hours of catecholamine stimulation compared with hCPCe but not significant at 6 hours. Similarly, increased eNOS phosphorylation in hCPCeβct compared with hCPCe at 2 and 6 hours, respectively. NS, nonsignificant, hCPCe vs. hCPCeβct *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. GFP, green fluorescent protein; GRK2, G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2; hCPC, human cardiac progenitor cell.
