Figure 1.
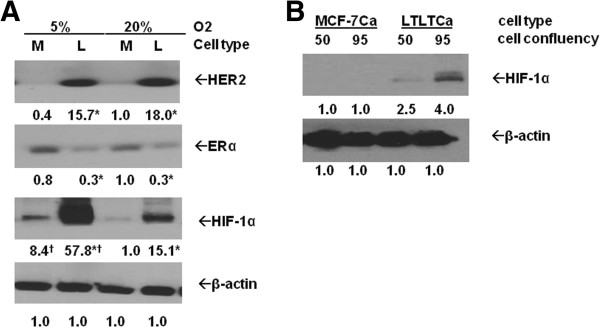
Comparison of protein expression in parental MCF-7Ca and LTLTCa cells under different oxygen tension and cell confluency. A) Parental MCF-7Ca and LTLTCa cells were plated and cultured in their respective passage media under either 5% O2 (in vivo normoxic/physiological conditions) or 20% O2 (normal, nonhypoxic cell culture conditions). Total protein was extracted and HER2, ERα, HIF-1α and β-actin were analyzed by Western blot analysis. Shown are representative blots and overall densitometry results of n = 6 independent cell samples/group. Densitometry results are expressed as mean fold-change in protein levels compared to MCF-7Ca cells in 20% O2 after normalization to β-actin (mean ± SD of n = 6 independent cell samples/group; *versus MCF-7Ca and † versus 20% O2; HER2 effect of cell type P = 0.0002, effect of % O2P = .5749, interaction between cell type and % O2P = .7337; ERα effect of cell type P <0.0001, effect of % O2P = .2879, interaction between cell type and% O2P = .2016; HIF-1α effect of cell type P = 0.0024, effect of % O2P = 0.0087, interaction between cell type and% O2P = 0.0413; two-way ANOVA). B) LTLTCa and parental MCF-7Ca cells were plated and cultured in their respective passage media at 1X or 2X density. Total protein was extracted when 2X density plates reached approximately 90% to 95% confluency, and, consequently, 1X density plates reached approximately 50% to 60% confluency. HIF-1α and β-actin protein were analyzed by Western blot. Densitometry results are expressed as mean fold-change compared to MCF-7Ca cells after normalization to β-actin. (mean ± SD, n = 6 independent cell samples/group; effect of cell confluency P = 0.0006, effect of cell type P < 0.0001, interaction between cell confluency and cell type P = 0.0006, two-way ANOVA). ANOVA, analysis of variance; ERα, estrogen receptor alpha; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 α subunit; n, number; SD, standard deviation.
