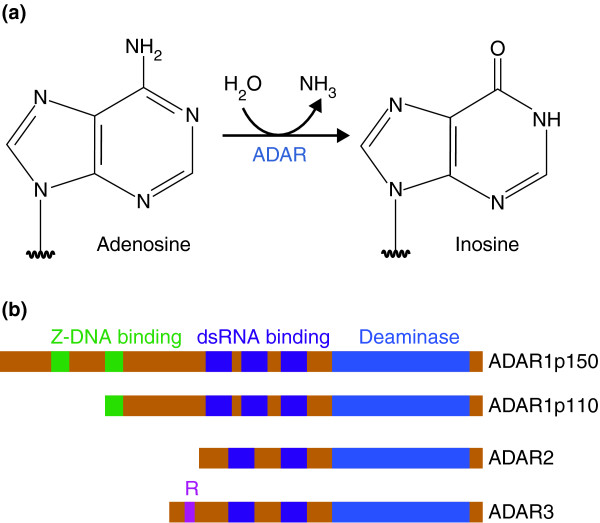
Figure 1.
Adenosine deamination and the ADAR enzyme family. (a) ADAR enzymes catalyze the A-to-I hydrolytic deamination reaction, by which an adenosine loses an amine group and is converted to inosine. (b) There are four main proteins of the ADAR enzyme family: two isoforms of ADAR1 (p110 and p150), ADAR2 and ADAR3. All of these enzymes contain a conserved deaminase domain, shown in blue. The double-stranded (ds)RNA-binding domains, shown in purple, determine substrate specificity. The two ADAR1 isoforms differ in their Z-DNA-binding domains, shown in green. ADAR3 contains an arginine-rich domain, shown in pink, which binds single-stranded RNA.