Figure 1.
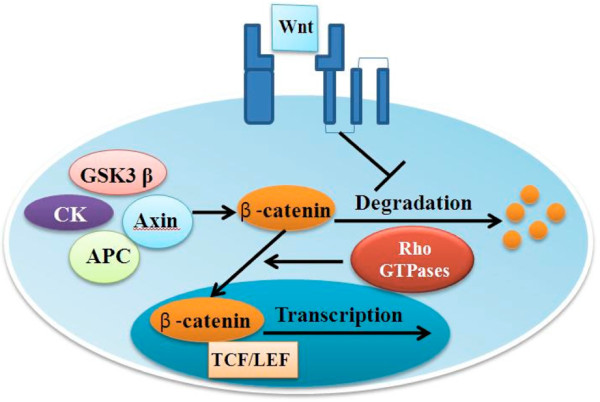
Schematic representation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. In canonical Wnt signaling, most β-catenin in the cytoplasm is sequestered in an oligomeric complex of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β), casein kinase (CK), axin and adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor protein (APC). When Wnt ligands bind to their cognate cell membrane receptors, signals are released to inhibit this degradation process, resulting in β-catenin accumulation and nuclear translocation regulated by Rac1, DKK1 and FRZB, which are all antagonists of canonical Wnt signaling. LEF, lymphoid enhancing factor; TCF, T cell factor.
