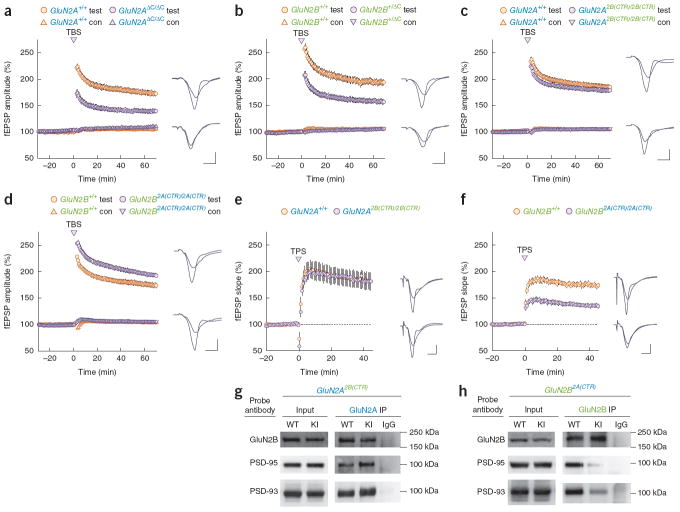
Figure 7.
Synaptic plasticity. Example fEPSPs recorded during baseline and 65 minutes after LTP induction in wild type (top) and mutant mice (bottom) are shown to the right in a–d. Calibration bars are 3 msec and 1 mV. Test, test pathway; con, control pathway. (a) Theta-burst induced LTP was significantly impaired (F(1,30) = 33.14, P < 0.0001) in GluN2AΔC/ΔC mice (129.9 ± 3.4%; n = 18, N = 5) compared to GluN2A+/+ mice (167.0 ± 4.5%; n = 25, N = 8). (b) Heterozygous truncation of the GluN2B CTR led to a significant decrease in theta-burst induced LTP (F(1,37) = 26.66, P < 0.0001) in GluN2B+/ΔC mice (148.9 ± 4.5%; n = 32, N = 10) compared to GluN2B+/+ mice (183.6 ± 5.6%; n = 21, N = 6). (c) Theta-burst induced LTP was intact in mice where the endogenous CTD of GluN2A protein was replaced with the CTD from GluN2B (F(1,39) = 1.60, P > 0.2). (d) Replacement of the endogenous CTD of GluN2B protein with the CTD from GluN2A led to a small but significant up-regulation of theta-burst induced LTP (F(1,39) = 6.67, P = 0.01) in GluN2B2A(CTR)/2A(CTR) (183.8 ± 4%; n = 34, N = 10) compared to GluN2B+/+ mice (169.6 ± 4.3%; n = 24, N = 9). (e) Theta pulse stimulation (TPS, 5 Hz/30 sec)-induced LTP was normal in GluN2A2B(CTR)/2B(CTR) mice t(9) = 0.041, P > 0.9). 45 minutes post-TPS fEPSPs were potentiated to (182 ± 6.4%; n = 12, N = 6) of baseline in slices from GluN2A2B(CTR)/2B(CTR) mice compared (182 ± 16%; n = 9, N = 5) of baseline in slices from GluN2A+/+ mice. (f) TPS-induced LTP was reduced in GluN2B2A(CTR)/2A(CTR) mutants t(12) = 6.76, P < 0.001. fEPSPs were potentiated to (135 ± 3.9%; n = 17, N = 7) of baseline in slices from GluN2B2A(CTR)/2A(CTR) mice compared to (172 ± 3.9%; n = 13, N = 7) of baseline in slices from GluN2B+/+ mice. Calibration bars in e and f represent 4 msec and 2 mV. (g) Normal levels of the MAGUK proteins were found in the input GluN2A2B(CTR)/2B(CTR) mice (PSD-95: t4 = 1.04; P > 0.3; PSD-93: t4 = 0.21; P > 0.8). Significant increases in PSD-95 (t3 = 13.1; P < 0.001) and PSD-93 (t4 = 4.1; P < 0.05) association were pulled down with the GluN2A2B(CTR) chimeric receptors. No significant difference in GluN2B protein was observed in the GluN2A2B(CTR)/2B(CTR) pull-downs (t4 = −0.3; P = 0.8). (h) Normal levels of the MAGUK proteins were found in the input of GluN2B2A(CTR)/2A(CTR) mice (PSD-95: t4 = −0.83, P > 0.4; PSD-93: t4 = −0.02, P > 0.9). Significantly reduced quantities of each of the two NMDAR-binding MAGUKs were pulled down with the GluN2B2A(CTR) chimeric receptor (PSD-95: t4 = −6.7, P < 0.01; PSD-93: t4 = −3.26, P < 0.05). No significant difference in GluN2B protein was observed in the GluN2B2A(CTR)/2A(CTR) pull-downs (t4 = −0.05, P > 0.9). n represents the number of slices that we used and N represents the number of mice.