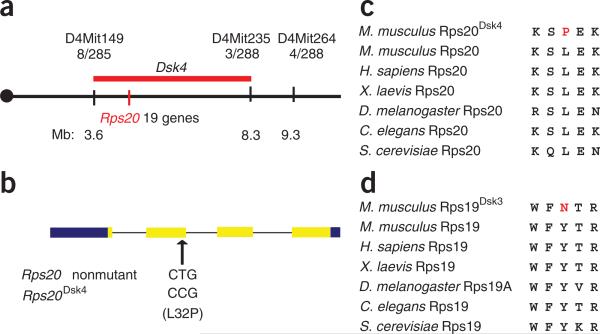
Figure 2.
Positional cloning of Dsk mutations. (a) Genetic and physical maps of the Dsk4 critical interval on mouse chromosome 4. Recombination frequencies (stated as the number of recombinant chromosomes between the marker and Dsk3, over the number of informative chromosomes evaluated) are given immediately below each marker. Approximate physical coordinates in megabases (Mb) are given below. (b) The position and sequence of the Dsk4 point mutation is shown relative to the exon–intron structure of Rps20 where untranslated and protein-coding regions are represented by blue and yellow, respectively. (c,d) Predicted protein sequences for Rps20Dsk4 (c) and Rps19Dsk3 (d), aligned with homologous sequence in other species.