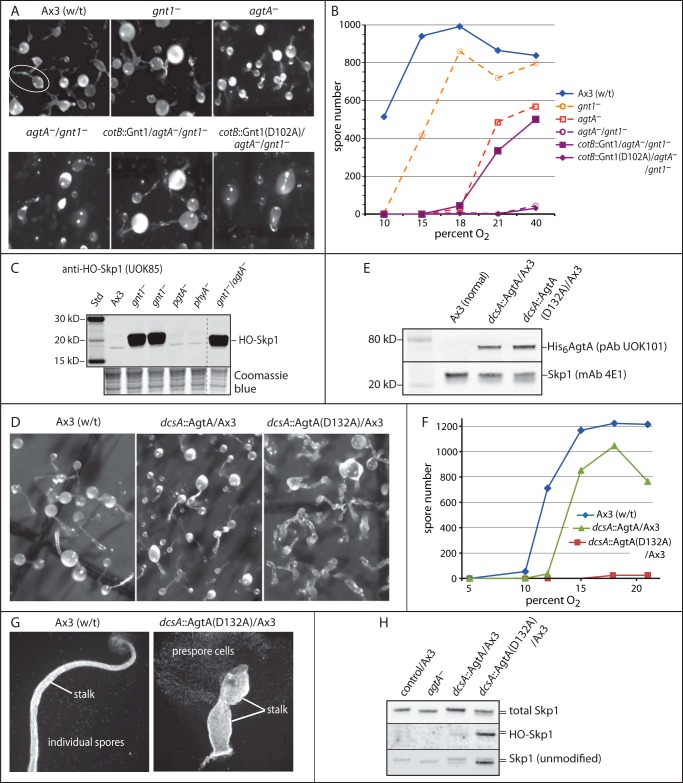
FIGURE 6.
Non-enzymatic activity of AgtA in vivo. A, representative images of development of wild-type (w/t) and mutant strains after 42 h at 21% O2. Normal and single knock-out strains are in the top row. The white oval encircles a typical fruiting body showing the spore-containing sorus linked to the stalk. The double agtA−/gnt1− mutant strain HW520 and strains complemented with normal or enzymatically inactive Gnt1(D102A) expressed under control of the prespore cell specific cotB promoter are in the bottom row. B, quantification of culmination, based on spore number, as a function of O2 in the atmosphere. C, Western blot analysis for HO-Skp1 in S100 extracts from growing cells of the agtA−/gnt1− double mutant strain compared with other mutant strains. The dashed line shows where other lanes from the same blot were omitted. The lower panel shows a region of the blotted gel after Coomassie Blue staining, as a loading control. D, representative images of development for 42 h at 21% O2 of strains constitutively overexpressing His6AgtA or enzymatically inactive His6AgtA(D132A) under control of the semi-constitutive dcsA promoter. E, a Western blot of growing cell S100 extracts from selected overexpression clones was probed with anti-AgtA, and with anti-Skp1 as a loading control. F, spore number as a function of the O2 concentration from strains shown in D. Data in B and D are representative of ≥3 independent trials where each strain was analyzed in parallel. G, examples of individual fruiting bodies from normal and AgtA(D132A)oe strains from panel D, imaged using fluorescent Calcofluor staining for the cellulosic cell walls of stalk and spore cells. Ax3(w/t) shows a typical slender stalk and spores that disperse during preparation. The AgtA(D132A)oe strain culminates to form a poorly organized bloated stalk, and the prespore cells remain contiguous because of failure to differentiate into spores. H, Western blots of S100 cell extracts from agtA−, His6AgtAoe, and His6AgtA(D132A)oe cells (in an Ax3 background) grown at 21% O2 were probed with anti-Skp1 antibodies that recognize total Skp1 (mAb 4E1), unmodified Skp1 (UOK87), or HO-Skp1 (UOK85). The slower migration of fully modified Skp1 relative to unmodified or hydroxylated Skp1 is denoted by the double bar.