FIGURE 3.
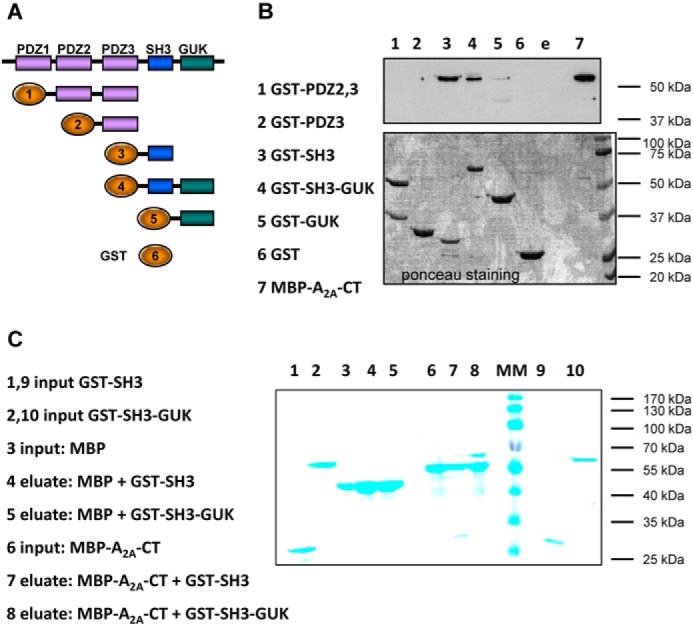
Binding of the C terminus of the A2A receptor fused to MBP to fusion proteins comprising the domains of SAP102 and GST. A, schematic of the domain structure of SAP102 and of the GST fusion proteins employed. The numbers correspond to the lanes of the gel shown in B. B, purified fusion protein comprising MBP and the carboxyl terminus of the A2A receptor (MBP-A2A-CT, 8 μg) was incubated in the presence of purified GST fusion proteins (8 μg each) comprising the indicated domains of SAP102 (lanes 2–5) or of GST (8 μg, lane 6) for 30 min at 4 °C in 0.1 ml of buffer. Proteins bound to GSH-Sepharose were released by denaturation. Aliquots corresponding to 25% of the eluate and MBP-A2A-CT (5% of the input, lane 7) were loaded onto a polyacrylamide gel, resolved electrophoretically, and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes that were probed with an antiserum directed against MBP (top panel). The bottom panel shows the corresponding nitrocellulose stained with Ponceau S to visualize the GST fusion proteins recovered in the eluate. C, MBP and the fusion protein MBP-A2A-CT (each at 8 μg) were incubated with fusion proteins comprising GST and the SH3 domain (GST-SH3) or the combined SH3-GUK domain (GST-SH3-GUK) of SAP102 (each at 8 μg) as described in B. The proteins were recovered by binding to amylose resin and released by denaturation. Aliquots corresponding to 10% of the input and 10% (MBP-A2A-CT) or 20% of the eluate (MBP) were applied onto and resolved on a polyacrylamide gel. Proteins were visualized by staining with Coomassie Blue. Shown are representative experiments that were reproduced twice.
