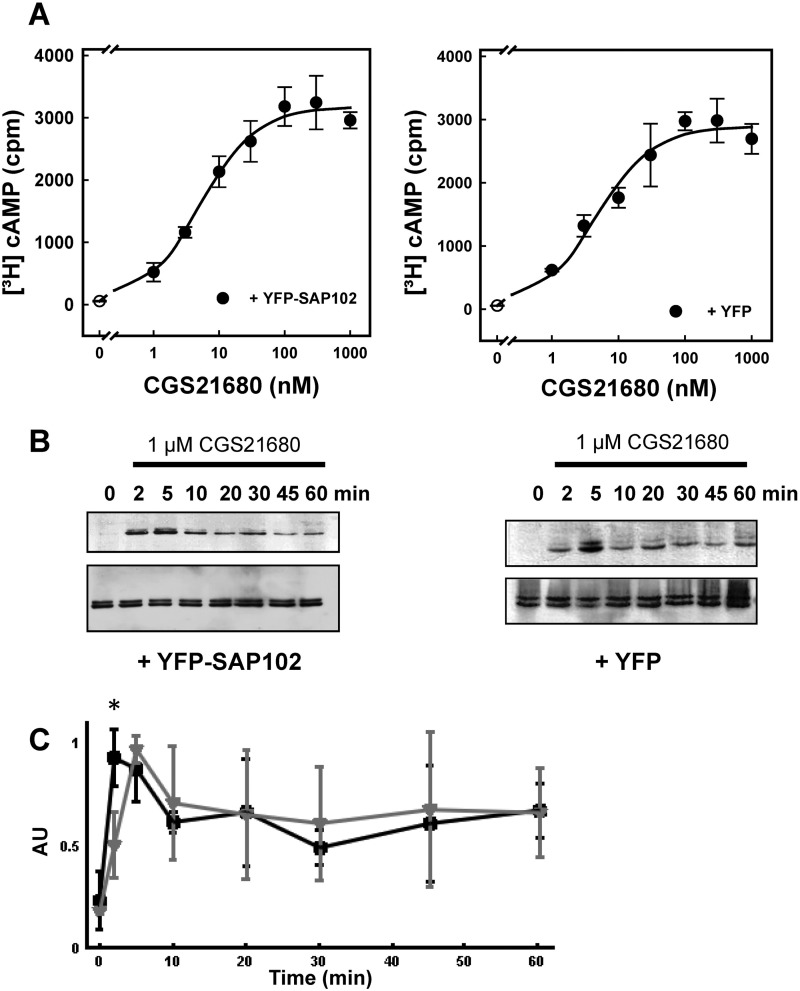
FIGURE 5.
Concentration-response curves for A2A receptor-dependent [3H]cAMP accumulation (A and B) and time course of A2A receptor-stimulated ERK phosphorylation in HEK293 cells in the absence and presence of coexpressed SAP102 (B and C). HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding the A2A receptor and either YFP-SAP (left panels) or YFP (right panels). A, cells (3 × 105/well) were labeled metabolically with [3H]adenine. After 16 h, fresh medium containing the indicated concentrations of CGS21680 was added, and cAMP production was stimulated for 20 min. Data are the means ± S.D. from three experiments. B, cells (3 × 105/well) were serum-starved for 16 h and subsequently stimulated with 1 μm CGS21680 for the indicated time intervals. Aliquots of cellular lysates (20 μg) were applied to SDS-polyacrylamide gels. After electrophoretic resolution and transfer to nitrocellulose, the level of active ERK1/2 was assessed by immunoblotting with an antiserum recognizing the dually phosphorylated active enzyme (p-ERK) (top blots) or an antiserum against holo-ERK1/2 (bottom blots) as loading control. C, the extent of ERK phosphorylation from three independent experiments carried out as shown in B was analyzed by densitometry. AU, arbitrary units. Data are means ± S.D. Gray triangles and black squares indicate the response seen in cells coexpressing YFP and SAP102, respectively. The initial response (i.e. ERK phosphorylation after 2 min) was significantly higher (*, p = 0.024, unpaired Student's t test) in the presence of SAP102.