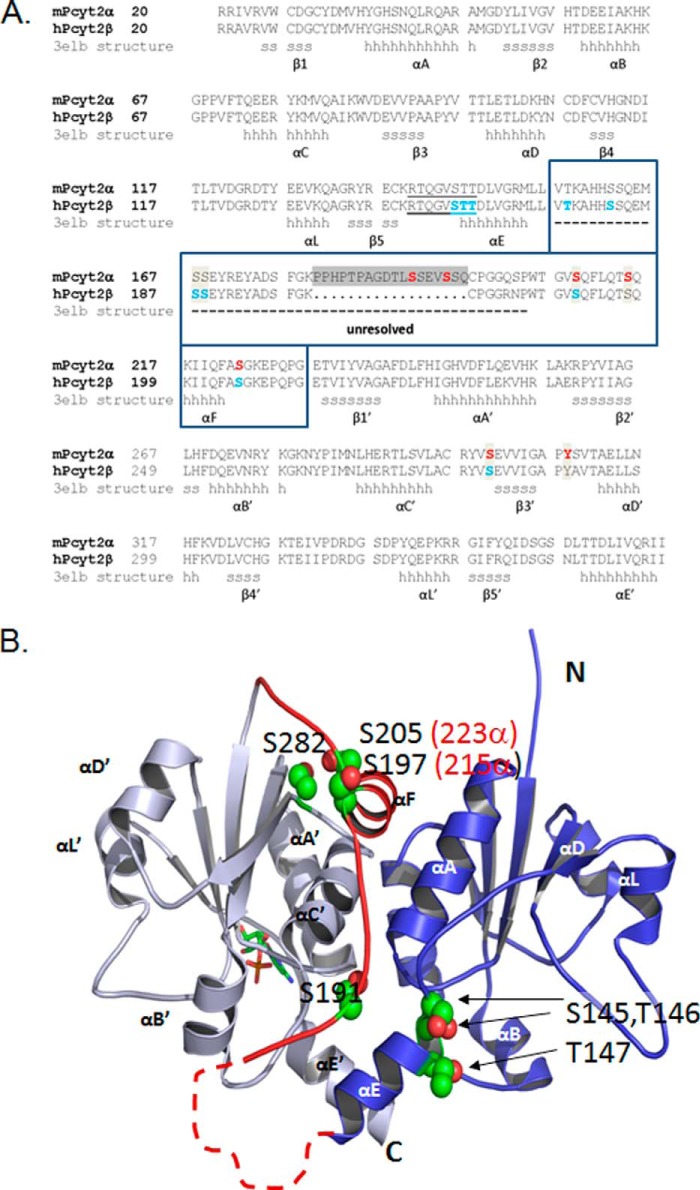
FIGURE 6.
Structural elements and new phosphorylation domains. A, sequence alignment of murine Pcyt2α (UniProt Q922E4) and human Pcyt2β (UniProt Q99447), is displayed. The structural elements for the human β isoform were obtained from Protein Data Bank code 3elb. N- and C-domains contain identical Rossman folds of six helices (αA to αE) and five β-sheets (β1 to β5); (h are α-helix residues and s are β-strand residues). The area unresolved in the Pcyt2β crystal is inside the boxed sequence, indicated by a dashed line, and includes the α-specific peptide (gray box). The identified phosphorylated residues are shown for mPcyt2α in red and for mPcyt2β in blue. B, phosphorylation sites mapped onto the solved structure of Pcyt2β. The image of human Pcyt2β (Protein Data Bank code 3elb) was prepared using PyMOL. The N-terminal catalytic domain is blue, and the C-terminal catalytic domain is in gray. A CMP ligand in stick representation occupies the active site of the C-cat domain. The linker region connecting the two domains is highlighted red. The side chains of the phosphorylated residues are shown as spheres (carbon, green; oxygen, red); the numbering is for Pcyt2β (Pcy2α numbering in parentheses). The broken line denotes the portion of the linker that is unresolved in 3elb and is not to scale. The unresolved segment contains residues 157–186 in Pcyt2β and residues 157–203 in Pcyt2α; these include identified phosphorylation sites at residues 157, 162, 167, and 168 in Pcyt2β and residues 192 and 195 in Pcyt2α.