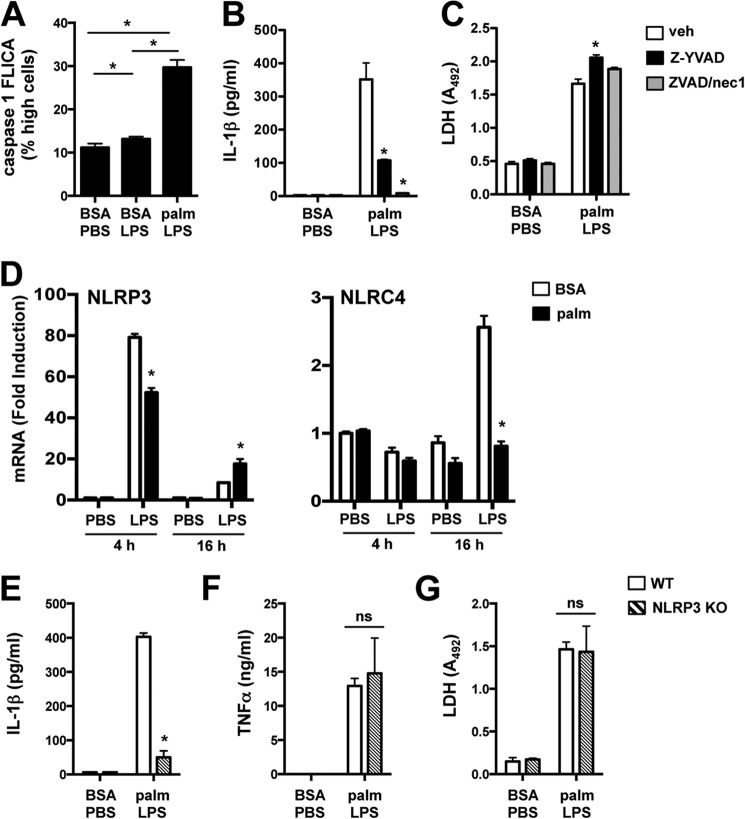
FIGURE 2.
Activation of the lipotoxic inflammasome occurs via a NLRP3-dependent mechanism. A, pMACs were stimulated with BSA-PBS, BSA-LPS, or palmitate (palm)-LPS for 16 h, and caspase-1 activation was determined by staining cells with caspase-1 FLICA reagent followed by quantification of FL1 high fluorescence cells by flow cytometry. B and C, macrophages were stimulated as indicated in the presence of Z-YVAD (50 μm, black bars) or Z-VAD/necrostatin 1 (nec1) (25 μm/50 μm, gray bars) for 20 h followed by quantification of IL-1β and LDH release. D, pMACs were pretreated with BSA or palmitate ± LPS for 4 or 16 h, and mRNA expression of NLRP3 and NLRC4 was determined by qRT-PCR. E–G, WT (white bars) or NLRP3 KO (hatched bars) pMACs were stimulated as indicated for 20 h, after which the release of IL-1β (E), TNFα (F), and LDH (G) was quantified. Bar graphs indicate the mean ± S.E. for a minimum of three experiments, each performed in triplicate. *, p < 0.05 for BSA versus palmitate, WT versus KO, or vehicle (veh) versus inhibitor.