FIGURE 2.
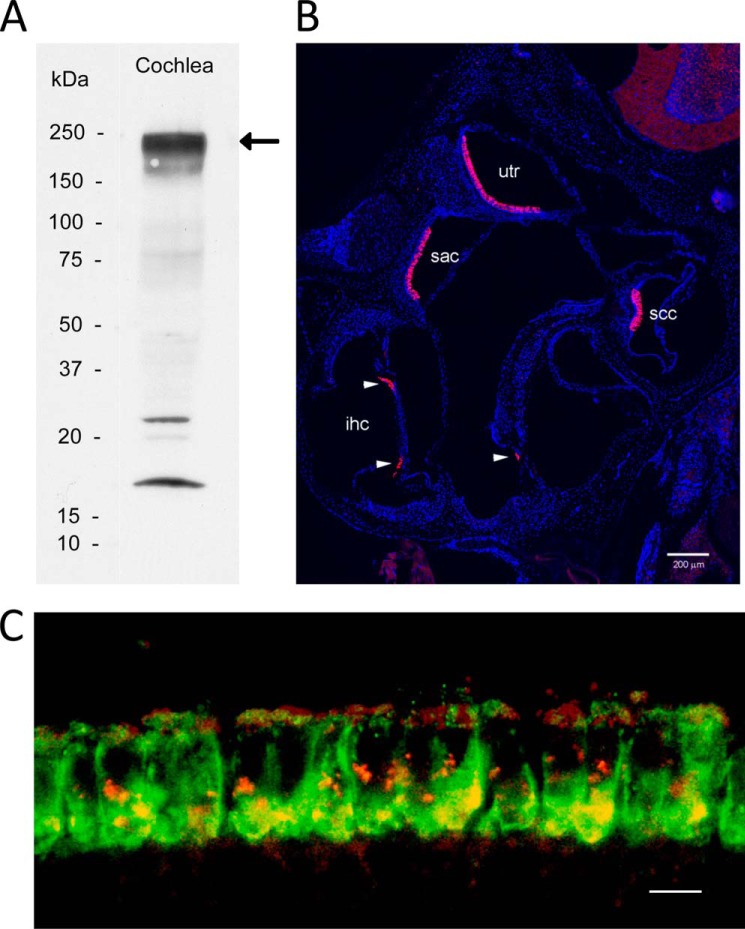
Otoferlin antibody specifically labels hair cells in mouse inner ear and co-localizes with the voltage-gated calcium channel CaV1.3 in cochlear inner hair cells. A, Western blot detection of otoferlin (220–240 kDa) in mouse cochlea (arrow). Positions of standards are labeled. B, confocal immunofluorescence images of the inner ear using an anti-otoferlin antibody (1:1,000; see text) and anti-rabbit secondary antibody conjugated with Alexa Fluor 546 (magenta) (1:6,000) counterstained with DAPI (blue) to label cell nuclei for purposes of orientation. The Zeiss Tile Scan tool was used to create a montage from a 20-μm cryostat section. All inner hair cells in all cochlear turns are labeled by the otoferlin antibody. Otoferlin also labels a subpopulation of hair cells in the vestibular sensory epithelia. utr, utricular macula; sac, saccular macula; ssc, semicircular canal; ihc, inner hair cell. Arrowheads designate inner hair cells. Scale bar, 200 μm. C, mouse organ of Corti double labeled with a custom rabbit polyclonal antibody described in the present study targeting mouse otoferlin sequence (green) and a goat polyclonal antibody targeting mouse CaV1.3 antibody (red). Voltage-gated calcium channel CaV1.3 immunofluorescence (red) is found primarily at basal and apical sites of cochlear inner hair cells (apical turn). Otoferlin immunofluorescence (green) is concentrated at the base of cochlear inner hair cells. The merged image (yellow) indicates sites on the basolateral membrane of cochlear inner hair cells where immunofluorescence of CaV1.3 and otoferlin overlap, consistent with co-localization and results for protein/protein binding. Scale bar, 10 μm.