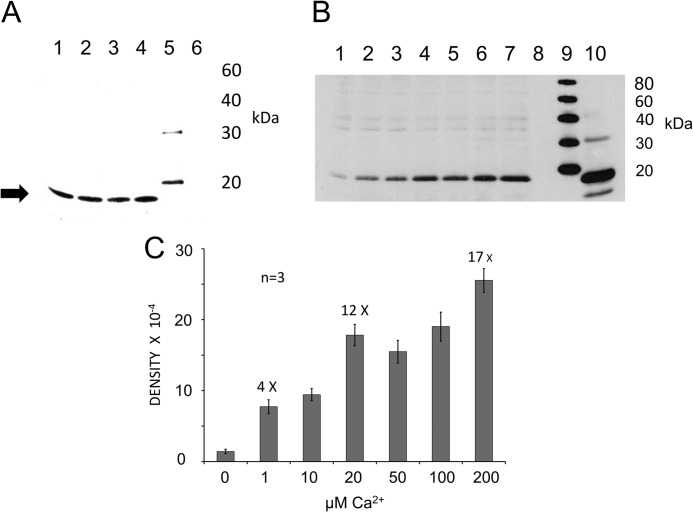
FIGURE 8.
Interaction of syntaxin-1 SNARE motif with C2 domains of otoferlin determined by pulldown assay. A, GST pulldown assay of the syntaxin-1 SNARE domain with GST-C2 domain fusion proteins as probes. Lane 1, GST-C2C; lane 2, GST-C2D; lane 3, GST-C2E; lane 4, GST-C2F; lane 5, standard; lane 6, GST alone as a negative control. The SNARE fusion peptide was detected with anti-Xpress antibody (Invitrogen) in a chemiluminescence reaction (Promega). A band is visible around 16 kDa (arrow), the predicted molecular mass of the SNARE domain plus the hexahistidine tag. All C2 domains examined interacted with the SNARE motif construct in the presence of 100 μm calcium in HBS binding buffer. B, the C2F/SNARE domain (syntaxin-1) interaction is Ca2+-dependent. In pulldown reactions, we added increasing quantities of Ca2+ to the binding buffer. After incubation and washing steps, the SNARE fusion peptide was detected in Western blots with anti-Xpress antibody. Calcium concentrations in the samples were 0, 1, 10, 20, 50, 100, and 200 μm for lanes 1–7, respectively. Lane 8 is a negative control (GST). Lane 9 shows molecular mass standards, and lane 10 signifies an aliquot representing ∼5% of the volume of the total SNARE lysate used in each binding assay. Reactions were carried out in HBS buffer after removing Ca2+ by Chelex-100 (see “Experimental Procedures”). There was minimal binding in the absence of Ca2+ (lane 1; 100 μm EGTA buffer with no added Ca2+), and the band intensity increased as Ca2+ increased (lanes 2–7). No band was detected in the GST control (lane 8). C, graph quantitatively showing the intensity of the Western bands for the C2F/SNARE interaction illustrated in B. Band intensities were estimated and averaged with GelQuant.NET software (Biochem Lab Solutions). The averages and S.E. (error bars) were plotted using Excel (Microsoft). At 0 μm Ca2+, there was minimum binding to the SNARE motif, and as the calcium increased to 1 μm, almost a 4-fold increase in band intensity occurred. By 20 μm Ca2+, the band intensity had increased 12-fold. Further increases in calcium concentration to 50 and 100 μm did not result in any significant increase in binding, although at 200 μm, a further increase (∼17-fold) was observed.