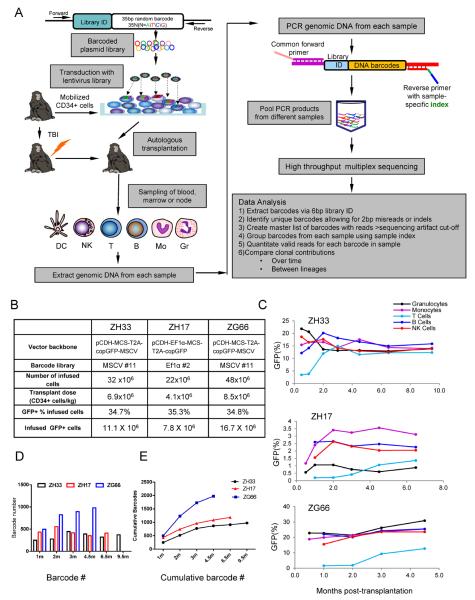
Figure 1. Experimental design and clonal diversity.
(A) Oligonucleotides consisting of a library ID followed by a random barcode were cloned into a lentiviral vector flanked by PCR primer sites. Mobilized PB autologous CD34+ cells were transduced and infused back into the irradiated autologous macaque, and PB, BM and lymph node samples were collected, purified by FACS, and barcode retrieval was performed via PCR and high throughput sequencing. Information relevant to methodologies presented in in Fig S1–S4 and Tables S1–S3. (B) Transduction and transplantation parameters for rhesus macaques ZH33, ZH17 and ZG66. (C) Percentage of GFP+ cells in PB lineages over time following transplantation. (D) Number of independent barcoded clones detected in the PB (combined B, T, Gr, Mono, NK) at each time point (m=months). (E) Cumulative number of independent barcoded clones detected in PB (combined B, T, Gr, Mono, NK) over time.