Fig. 4. IL6 treatment enhances MUC13 expression via the JAK2/STAT5 pathway.
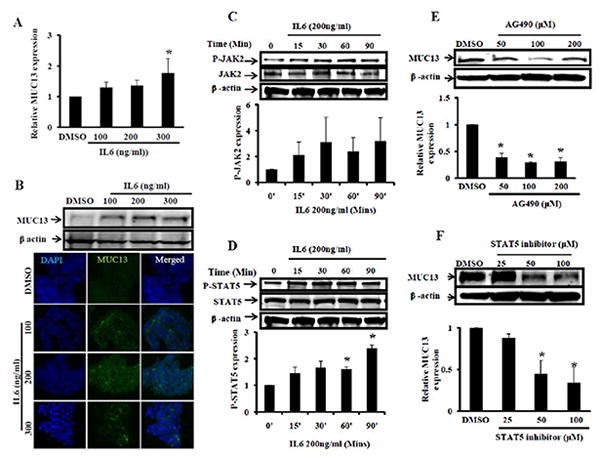
(A and B) IL6 increases MUC13 expression HT-29 cells were serum starved and treated with IL6 (100-300 ng/ml) and vehicle control (DMSO) for 48-72 hrs. A) At 48 hrs RNA was isolated and analyzed by Q-RT-PCR for MUC13 expression. B) At 72 hrs cell lysates were collected and analyzed by Western blot (top) or cells were fixed and processed for immunofluorescence analysis (bottom). (C and D) IL6 treatment increases P-JAK2 and P-STAT5 expression: Cells were treated with IL6 (200 ng/ml) or DMSO for 15-90 mins after an 8 hr serum starvation. SDS lysates were collected and subjected for Western blot analysis to detect total JAK2, P-JAK2 (4C), total STAT5 and P-STAT5 (4D) expression. Quantification of P-JAK2 and P-STAT5 expression is shown below corresponding Western blots. (E and F) Treatment with JAK2 and STAT5 inhibitors attenuated MUC13 expression: Cells were serum starved for 8 hrs and then treated with JAK2 (AG490) and STAT5 inhibitors. Cells were further treated with JAK2 and STAT5 inhibitors in the presence of IL6 for 48-72 hrs. Expression of MUC13 was detected by Western blot analysis following treatment with JAK2 inhibitor (4E) and STAT5 inhibitor (4F). Quantitative analysis is shown below corresponding Western blots. All experiments were repeated at least two times and representative blot is shown. Bar indicates the mean, error bar indicates the SEM, * P<0.05.
