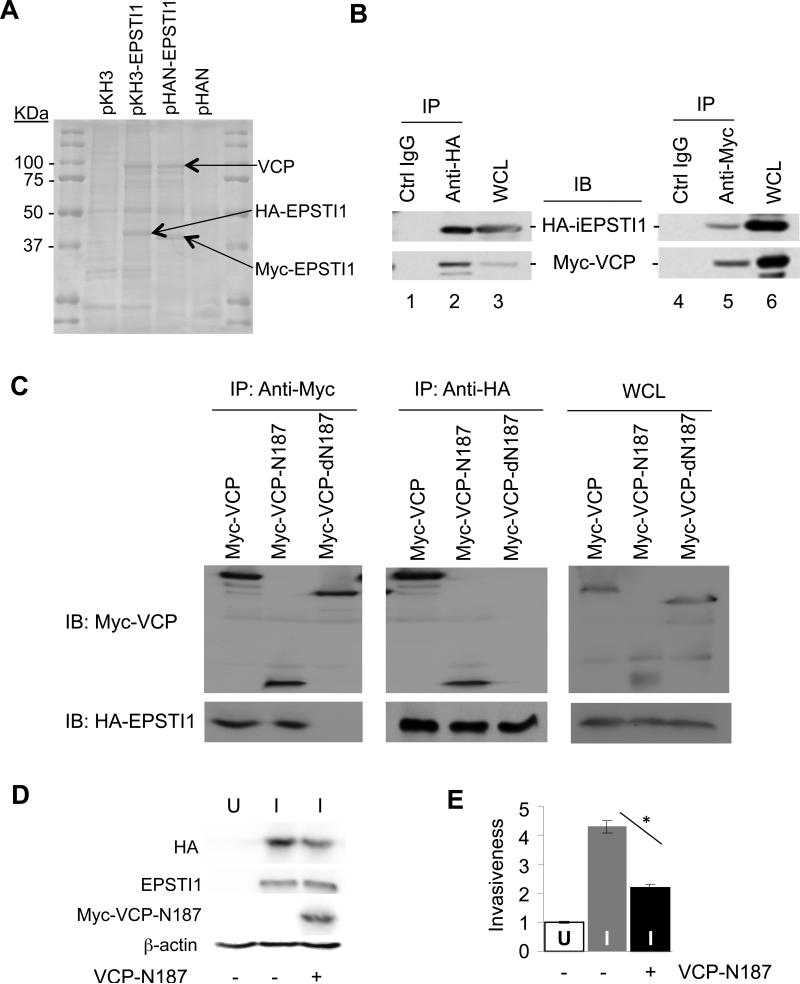
Figure 6.
EPSTI1 interaction with the 1-187 aa region of VCP (VCP-N187) is critical for the cell invasion. (a) Mass spectrometry identified VCP as an EPSTI1 interaction protein. Plasmid encoding HA- or Myc-tagged EPSTI1 (pKH3-EPSTI1 or pHAN-EPSTI1) or the control vector was transfected into HEK293ft cells for 24 h, followed by anti-HA or anti-Myc coIP and subsequent mass spectrometry as described in the Materials and Methods. (b) CoIP verification of interaction between EPSTI1 and VCP. The HEK293ft cells were cotransfected with pKH3-EPSTI1 and pHAN-VCP for 24 h and prepared for CoIP and western blotting. WCL, whole cell lysate. (c) VCP-N187 is where EPSTI1 binds. The full-length VCP, its N-terminal 187 residual fragment (N187) or its C-terminal half (dN187) was co-transfected and Co-IP were followed similarly as described in b. (d and e) VCP-N187 is crucial for EPSTI1 to promote the cell invasion. The MCF7-iE1 cells were grown under U or I conditions for 24 h. The I-cells were then transfected with the VCP-N 187 peptide or the control vector for another 24 h prior to western blotting (d) or Matrigel invasion assay (e, *P < 0.05).