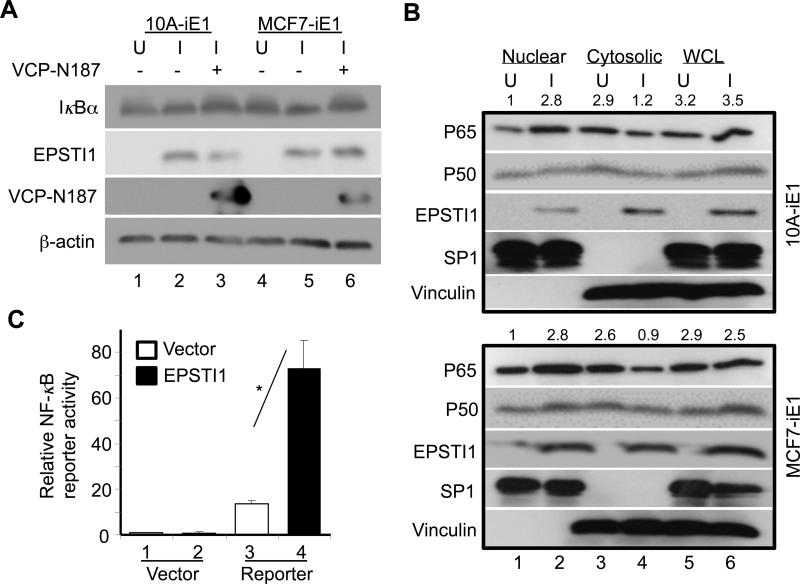
Figure 7.
EPSTI1 interaction with VCP is critical for the activation of NF-κB. (a) EPSTI1 expression decreases the expression of IκBα depending upon its binding to CVP. The 10A-iE1 or MCF7-iE1 cells were cultured under U or I conditions for 24 h. The I-cells were then transfected with the VCP-N187 peptide (lanes 3 or 6) or the control vector (lanes 2 or 5) for another 24 h prior western blotting. (see Figure S2A for quantitative data). (b) EPSTI1 expression promotes the nuclear translocation of NF-κB. The 10A-iE1 or MCF7-iE1 cells were cultured under U or I conditions for 24 h. Then the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were isolated for western blotting. SP1 and vinculin were used as a marker for nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively. (see Figure S2B and S2C for quantitative data). (c) EPSTI1 expression increases the transcriptional activity of NF-κB. MCF7 cells were co-transfected with the NF-κB reporter or control vector with EPSTI1 or control vector for 24 h before luciferase activity was determined. Data are representatives of at least three independent experiments in duplicate. *P < 0.05.