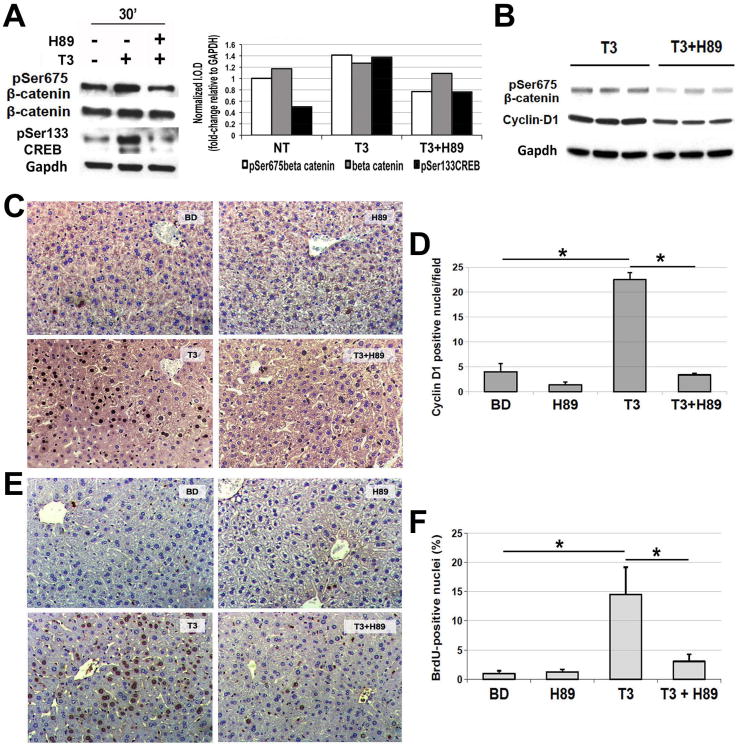
Figure 5. Blockade of Protein Kinase A impairs T3's effect on β-catenin, Cyclin-D1 and hepatocyte proliferation in mice.
A. A representative western blot using pooled samples from three wells per condition (left) shows increased levels of pSer675-β-catenin and pSer133-CREB in primary mouse hepatocytes after 30 minutes of T3 treatment. Inclusion of PKA inhibitor H89 (1 μM) in the media 30 minutes prior to the addition of T3 (100 nM) showed a notable decrease in pSer675-β-catenin and pSer133-CREB levels. Densitometry on the representative WB (right) shows an increase in pSer675-β-catenin and pSer133-CREB after T3 treatment, which was blocked by H89 treatment. (I.O.D. – integrated optical density).
B. A representative western blot shows a decrease in the hepatic levels of pSer675-β-catenin and Cyclin-D1 when H89 was injected twice IP in 3-day T3 fed mice as compared to 3 day T3 only group. Gapdh verifies equal loading. Each lane represents an individual sample.
C. A representative micrograph (200×) illustrates a decrease in the number of Cyclin-D1-positive hepatocytes when H89 was injected twice to the 3-day T3-fed mice as compared to T3 only group. Three or more mice per group were used for this study.
D. Quantification of the Cyclin-D1-positive hepatocytes shows a significant decrease in positive cells in H89+T3 as compared to T3 only group (*p<0.05).
E. A representative micrograph (200×) illustrates a noteworthy increase in BrdU uptake by the hepatocytes in mice after 5 days of T3 feeding, which was dramatically decreased in animals simultaneously administered H89 IP every 24 hours. Three or more mice per group were used for this study.
F. Quantification of BrdU positive hepatocytes shows a significant (*p<0.05) decrease in the LI in T3+H89 group as compared to T3 only.