Figure 2.
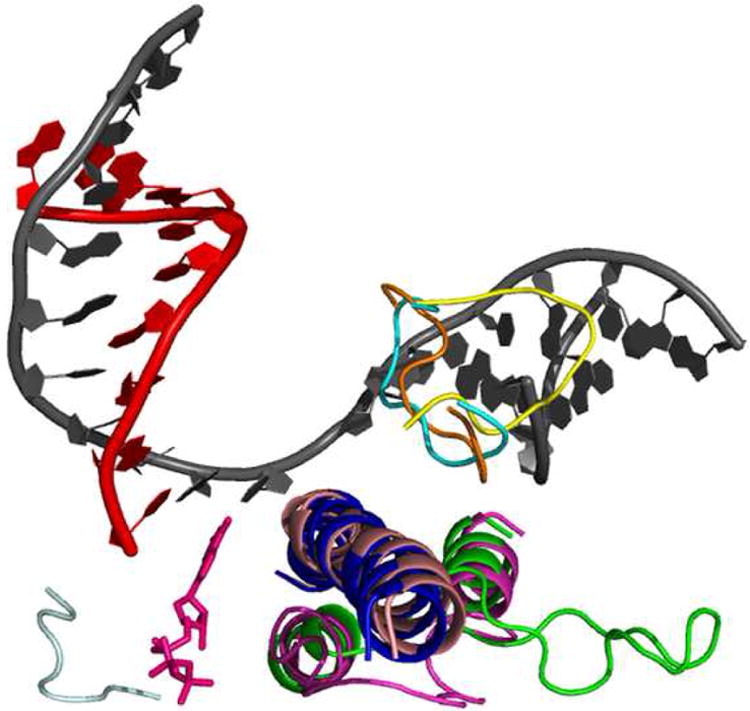
Conformational changes in the S. cerevisiae EC thought to be involved in translocation. Shown are the different conformations of the trigger loop, bridge helix, and fork loop 2. The trigger loop can adopt an open (green, PDB:1Y1V) and closed (magenta, PDB:2E2H) conformation. When closed, the trigger loop contributes several residues that are essential for catalysis. The bridge helix can adopt a bent (light pink, PDB:2VUM) and unbent (blue, PDB:1Y77) state. Fork loop 2 has been seen in three distinct conformations: open (yellow, PDB:2E2I), partially closed (orange, PDB:1Y1V), and closed (cyan, PDB:1Y77). The DNA strands are in grey and the RNA is red. The catalytic nucleotide (pink) is shown bound to the catalytic residues (light grey).
