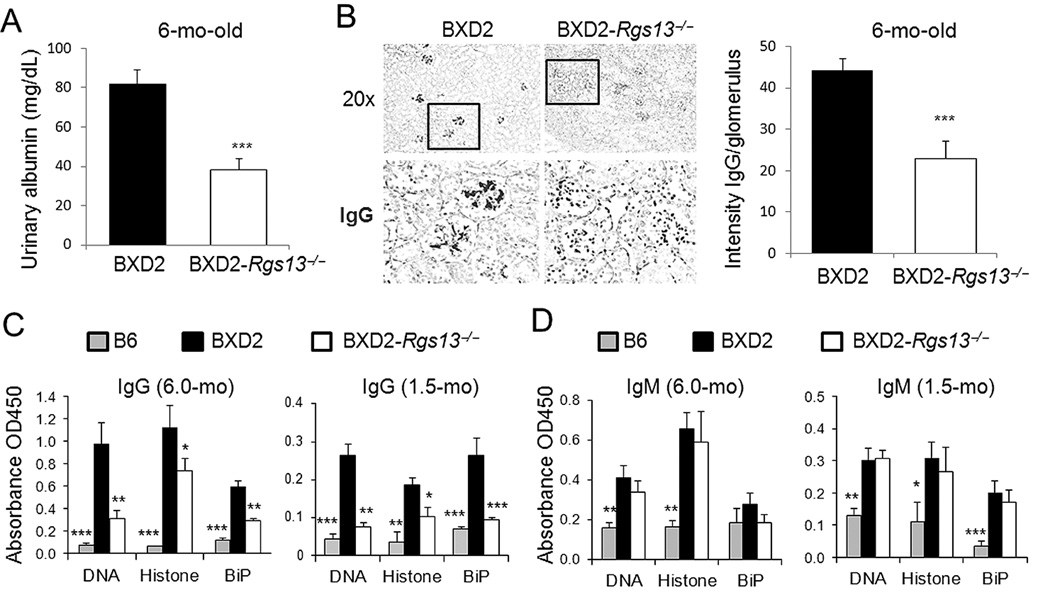
Figure 3.
Kidney disease and production of pathogenic IgG autoantibodies are reduced in BXD2-Rgs13−/− mice. A, ELISA analysis of urinary albumin in 6-mo-old mice (N=6, ***p<0.005). B, Left: Representative photomicrographs of immunohistochemical staining of IgG antibody deposits on glomeruli. Objective lens was 20×. Box indicates area that was enlarged and shown in lower panels. Right: ImageJ quantitation of the intensity of IgG deposits in glomeruli of the indicated strain at 6-mo of age. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. At least 4 kidney sections were examined per mouse, and staining of at least 10 glomeruli quantified for each kidney section. C, D, ELISA analysis of serum levels of (C) IgG and (D) IgM autoantibodies in the indicated strains at 6.0-mo and 1.5-mo of age (mean ± SEM, N=6–10 mice/group; * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.005 for results for each strain in comparison with age-matched BXD2-WT mice).