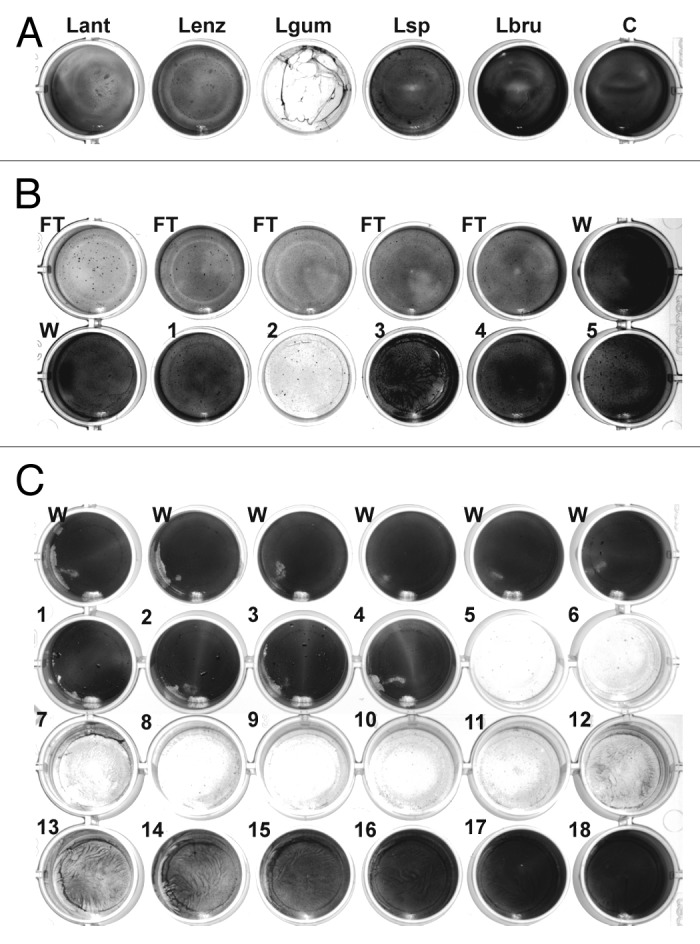
Figure 1. Detection and chromatographic characterization of biofilm-degrading activity from L. gummosus. (A) Crude extracts prepared from the extracellular material of different Lysobacter species grown for 3 d on solid medium were tested against S. epidermidis biofilms on 24-well plates. Lant, L. antibioticus; Lenz, L. enzymogenes (DSMZ 2043); Lgum, L. gummosus; Lsp, Lysobacter sp. (DSMZ 3655); Lbru, L. brunescens; C water control. (B) L. gummosus extract was loaded onto a Q Sepharose Fast Flow column, and eluted isocratically with 100 mM NaCl (fractions 1–5). The flow-through (FT), the wash fractions (W), and the elution fractions were tested for biofilm-degrading activity. (C) The active fraction from the Q Sepharose column was passed over a Mono S 5/50 GL column and subsequently loaded on a Mono Q 5/50 GL column. Fractions 1–18 were eluted with 0–225 mM NaCl and tested for biofilm-degrading activity.
