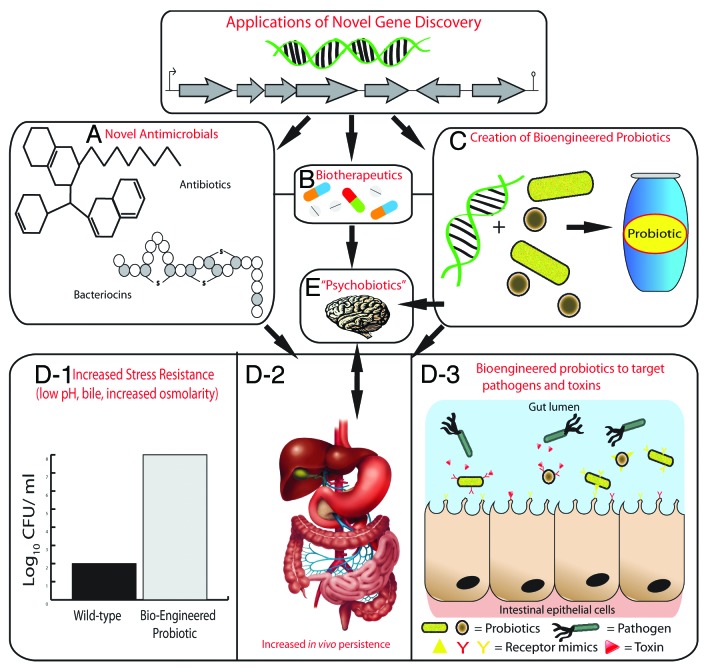
Figure 2. Applications of novel genes discovered by metagenomics. Novel genes or gene clusters discovered through metagenomics will encode proteins for the production of novel antimicrobial compounds such as antibiotics and bacteriocins (A) and biotherapeutics (B). Novel genes may also be used to create bioengineered probiotic strains (C). Bioengineered probiotics can be created that are more resistant host-associated stresses of the gastrointestinal tract such as low pH, bile, and increased osmolarity (D-1), which will lead to increased survival and persistence in the gastrointestinal tract (D-2). This will ultimately increase their therapeutic efficacy; using them to target specific pathogens or toxins by expressing receptor-mimic structures on their surface, thus preventing infection (D-3). The use of probiotics that have a health benefit to persons with a psychiatric illness have been termed “psychobiotics”. The creation of bioengineered psychobiotics that can produce neuroactive compounds at an increased level or for a specific illness may be possible by identifying novel genes through metagenomics (E).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.