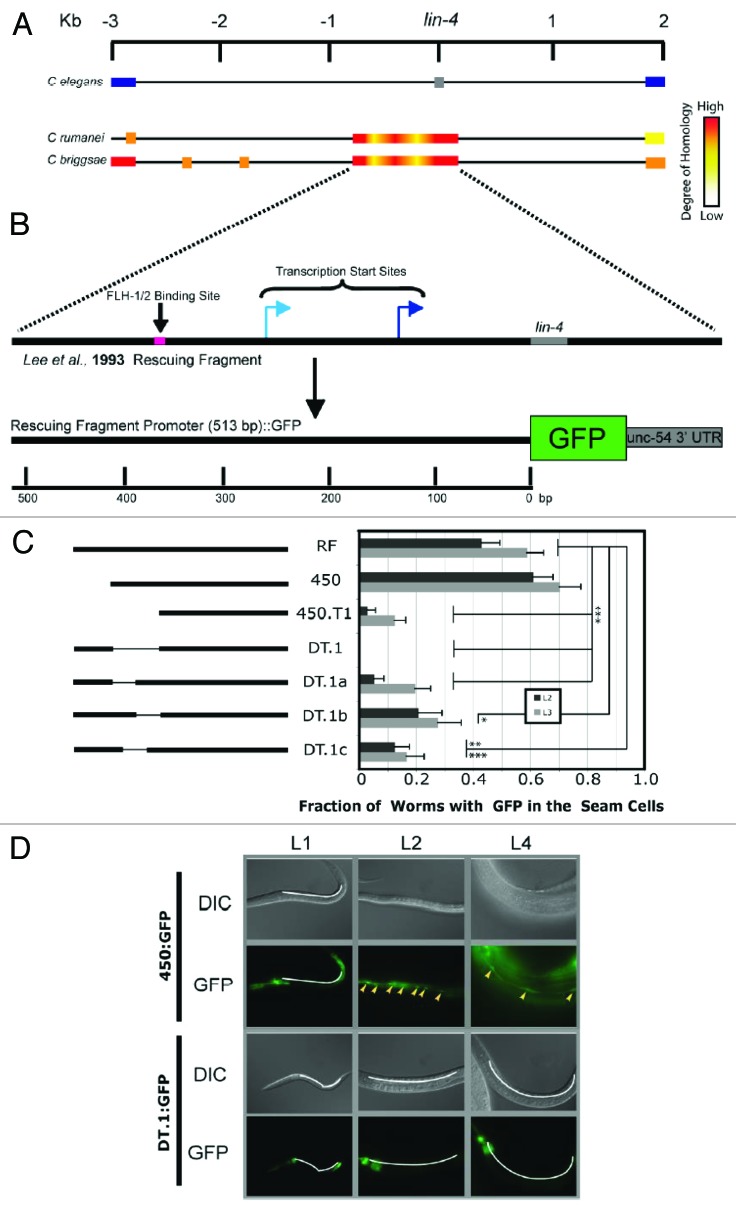
Figure 1. A cis-acting element required for the transcription of lin-4. (A) Schematic illustration showing an alignment of the intronic sequence flanking lin-4 in the C. elegans genome (reference sequence) with the lin-4 locus of C. remanei and C. briggsae. The C. elegans graphic shows the position of the lin-4 sequence (gray box), as well as flanking exons of the host gene, F59G4.1 (blue boxes). C. remanei and C. briggsae schematics are shown using a heat bar to illustrate sequence homology at and around the lin-4 locus with the lin-4 locus in C. elegans. Sequence lengths are measured in kilobases (Kb). (B) Schematic illustration of the composition of the transcriptional fusion construct used to elucidate cis-acting regulatory elements in the putative lin-4 promoter.24 A short DNA sequence shown to rescue the lin-4-mutant phenotype is shown, within which is contained an FLH-1, -2 binding site (pink box), lin-4 (gray box), and 2 transcriptional start sites.4,22,23 The transcriptional start site represented by the dark blue arrow was independently verified in our laboratory. Homologous sequence upstream of the lin-4 mature sequence was fused to GFP, as previously described.24 Promoter length is measured in base pairs (bp). (C) On the left, an illustration of the promoter regions used to drive GFP expression in C. elegans. Truncations to, and deletions from, the original rescuing fragment promoter (RF) are indicated. On the right, transgenic lines developed with these constructs were assayed for expression of GFP in the seam cells. No GFP was seen in embryo and L1 animals, and the fraction of animals expressing GFP in the seam cells in stages L2 and L3 are indicated. Error bars represent the standard error of the proportion. Significance was measured using a z test, with calculated P values as indicated (*P < 0.005; **P < 0.0015; ***P < 0.00007); 23 < n < 73. (D) Images showing GFP expression in seam cells over 3 larval stages of development (L1, L2, L4). The DNA construct used to develop the transgenic lines is depicted at the left. Seam cells positive for GFP expression are indicated (yellow arrowheads). White lines indicate the regions where seam cells are found in GFP-negative animals.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.