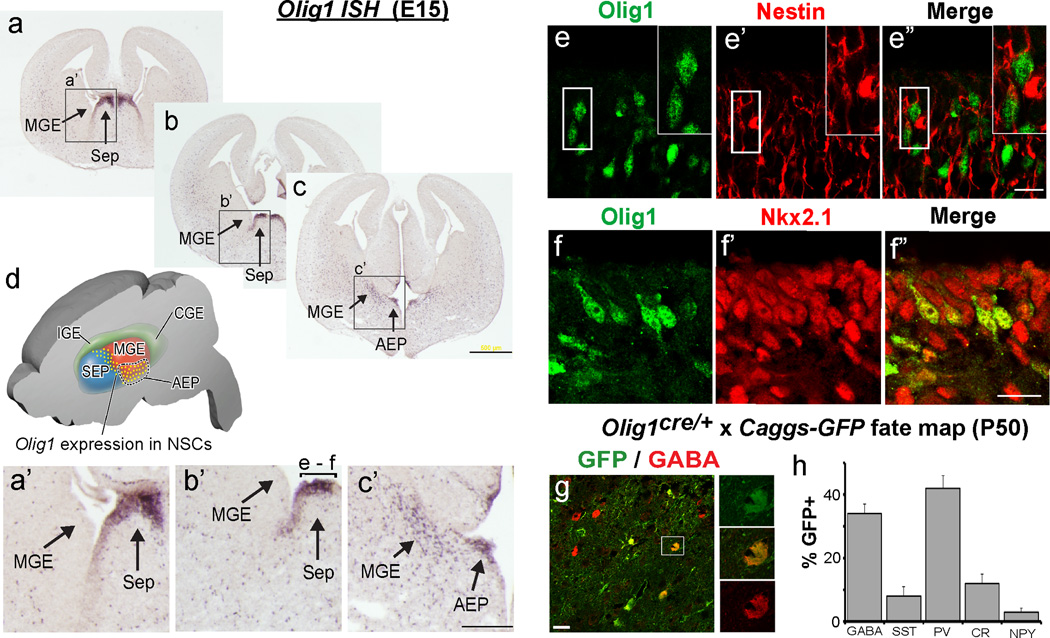
Figure 3. Olig1 is expressed in ventral telencephalic progenitors for interneurons.
(a–c) Anterior to posterior serial sections of in situ hybridization for Olig1 demonstrating expression in the ventricular zone (VZ) of dorsal embryonic septum (sep), ventral medial ganglionic eminence (vMGE) and anterior enteropeduncular area (AEP). (d) A cartoon of the domain in which Olig1 is expressed in the ventricular zone. (a’–c’) Higher magnification view of the regions expressing Olig1. These regions are denoted by the boxes and arrows in panels a–c. The bracket labeled e-f in image b’ defines the regions shown in panels e–f. (e) Confocal projections showing that Olig1 (green, e) colocalizes the radial glia protein Nestin (red, e’; merged image e”). (f) Confocal projections showing that Olig1 (green, f) colocalizes Nkx2.1+ progenitors (red, f’; merged image f”) which are known to give rise to both INs and OLs. (g) Representative image of fate mapping in cerebral cortex from Olig1cre/+ mice crossed to the Caggs-Gfp reporter mouse, showing approximately ~35% of GABA+ INs (red) are derived from Olig1+ progenitors as defined by the expression of the GFP+ (green) reporter protein. (h) Quantification of the proportion of a panel of IN markers (GABA, PV, SST, CR, or NPY) colabeling GFP (percentage +/− SEM). Note the preferential labeling of PV+ subtypes. (c) scale bar = 500 µm, (c’) scale bar = 200 µm, (e”,f”) scale bar = 20 µm. Additional abbreviations: lge, lateral ganglionic eminence; cge, caudal ganglionic eminence.