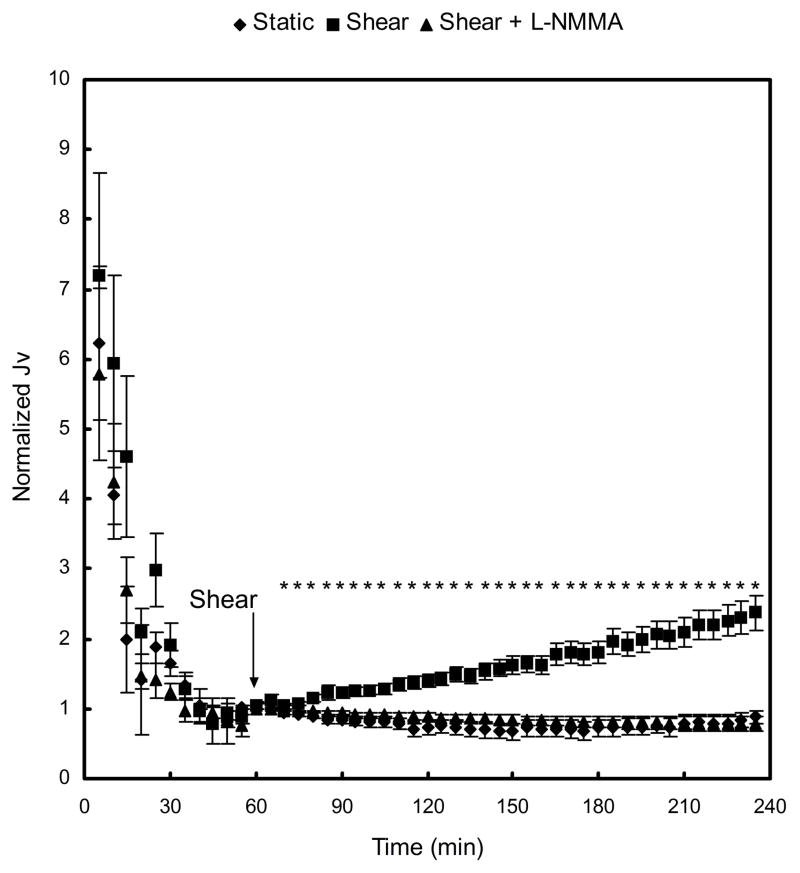
Fig. 1.
Effect of short term-shear stress on water flux (Jv). At time 0 min, a hydrostatic pressure differential of 10 cm H2O was applied, and a baseline was established after 60 min. Application of shear stress at 60 min triggered a time-dependent increase in Jv, which was blocked by a treatment of BAEC monolayers with 50 μM L-NMMA. Baseline Jv for static control, shear, and shear + L-NMMA were 1.97 ± 0.33 ×10−6 cm·s−1 (n=7), 2.27 ± 0.23 ×10−6 cm·s−1 (n=7), and 3.04 ± 0.55 ×10−6 cm·s−1 (n=7), respectively. * P < 0.05, significant differences between shear and static monolayers. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.