Figure 8.
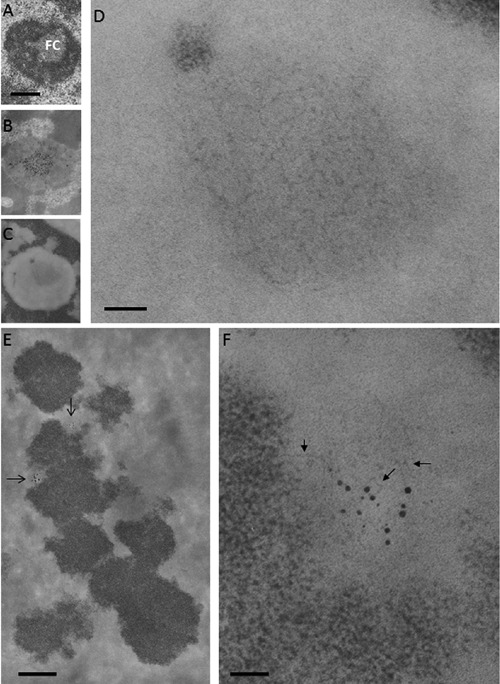
Ribosomal chromatin. A, B, C) Human circulating lymphocytes; scale bar: 0.4 μm. A) Aldehyde and osmium fixation, uranium and lead staining: a solitary, large fibrillar center (FC) is present in the central area of the nucleolus. B) En-bloc silver staining for the visualization of proteins associated to the ribosomal genes; thin section stained with uranium and lead: silver deposits are mainly located in the FC. C) Feulgen-like osmium ammine reaction: in the nucleolus, a light electron-opaque area is located in the same central zone occupied by the fibrillar center. D) Detail of (C) showing that the central area of the nucleolus is occupied by a large agglomerate of extended DNA filaments with a thickness of 2-3 nm; scale bar: 50 nm. E,F) En-bloc silver staining for the visualization of the proteins associated with the ribosomal genes in metaphase chromosomes; thin section stained with the Feulgen-like osmium-ammine reaction. E) Silver grain deposits identify two nucleolar organizer regions (arrows); scale bar: 10 μm. F) Detail of (E) showing that chromatin associated with the silver grains is composed of thin DNA filaments (arrows), similar to the fibrillar centers of interphase nuclei; scale bar: 50 nm.
