Figure 1.
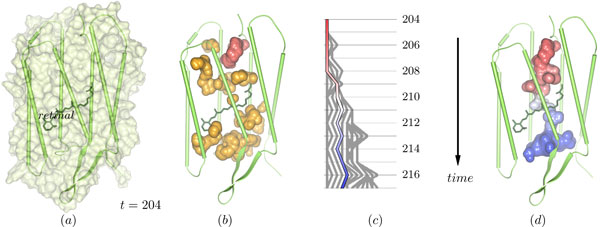
The cavity structure in a bacteriorhodopsin monomer. (a) The monomer at time step 204 is depicted by its surface and secondary structure cartoons. The small structure in the middle of the monomer, shown by its bonds, is the retinal, which is covalently bound to Lys216. (b) Depicted are all cavities that were found in time step 204. From the red cavity, the tracing is started (see panels (c) and (d)). (c) Split and merge graph showing the path tracing started at the red cavity in (b). (d) The selected path in (c) started at the red cavity leads to the dynamic molecular path depicted in this image. The path connects the cytoplasmic (top) and the extracellular side (bottom).
