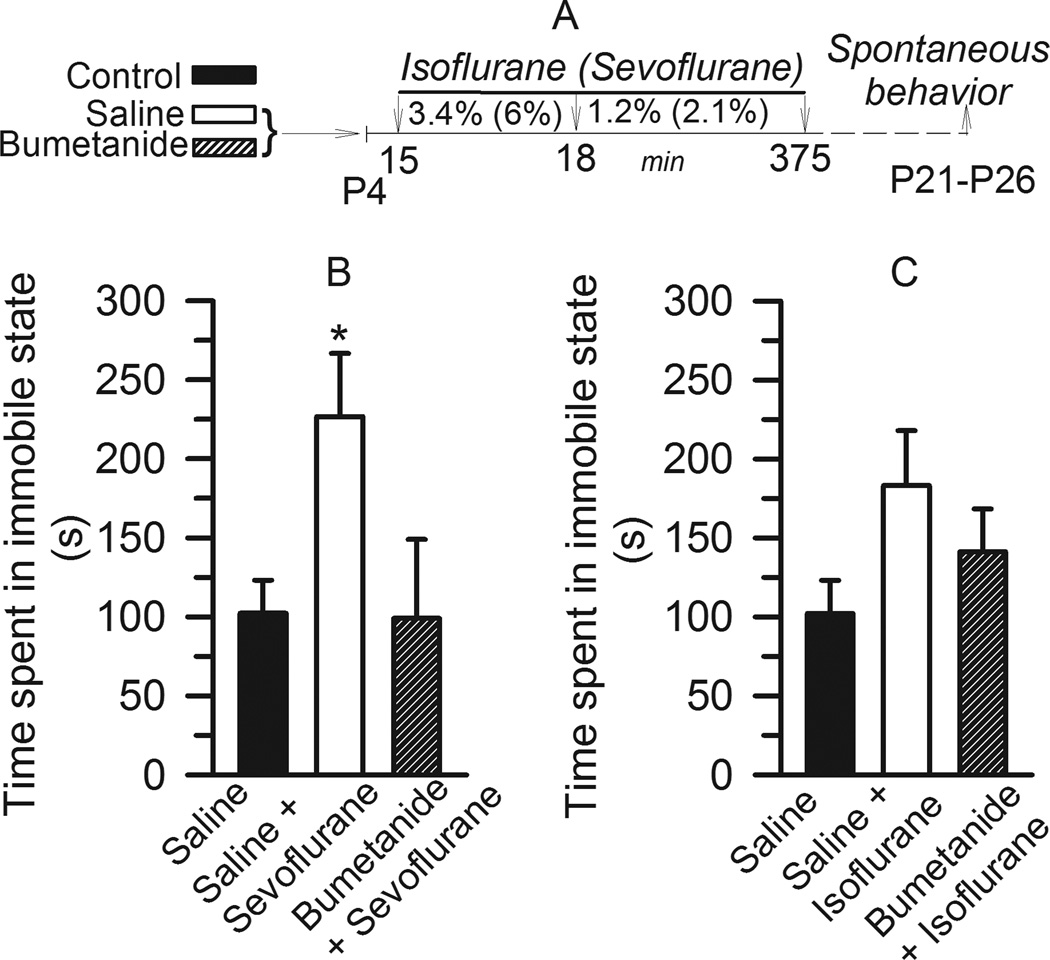
Figure 3.
Rats that were anesthetized with sevoflurane on postnatal days 4–5 (P4–P5), but not isoflurane, spent significantly increased time in immobile state; an effect that was alleviated by pretreatment with bumetanide. A: Illustration of the experimental protocols. B: The effect of isoflurane. Histogram showing time spent in immobile state in three experimental groups: Rats in the two treatment groups were exposed to isoflurane anesthesia after they were pretreated with either bumetanide (5 µmol/kg, intraperitoneally, n=12 per) or equal volume of saline (n=12). Rats in the control group (n=19) did not undergo anesthesia at P4. C: The effect of sevoflurane. Histogram showing time spent in immobile state by three treatment groups: 1) control (n=19); saline + sevoflurane (n=13) and bumetanide + sevoflurane (n=10). *, P<0.05 vs Control. All non-anesthetized rats tested in spontaneous behavior experiments were combined in the control groups.