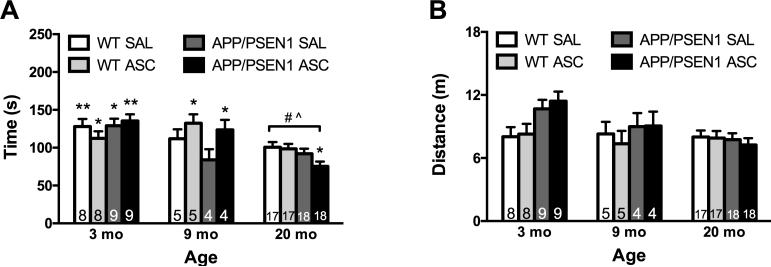
Figure 2.
Intravenous ASC improved short-term spatial memory in APP/PSEN1 and WT mice aged 9 months. A) The time spent exploring the novel arm of the Modified Y-maze decreased significantly with age as mice aged 20 months were significantly impaired relative to mice aged 3 (p < .001) and 9 months (p < .05). ASC treatment significantly improved spatial memory in 9 month-old APP/PSEN1 and WT mice (p < .05). No other effects of genotype or ASC treatment were reported. B) Total exploration was not affected by ASC treatment, although 3 month-old mice covered significantly more distance than 20 month-old mice (p < .05). This effect was mainly due to elevated activity in 3 month-old APP/PSEN1 mice. Values are mean ± SEM. Numbers on bars indicate group size. * p < .05; ** p < .01 in a One-Sample T Test comparing time in the novel arm to chance (100 sec). # p < .001 compared to all 3 mo mice; ^ p < .05 compared to all 9 mo mice.