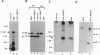Abstract
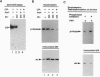
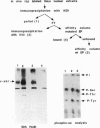
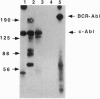
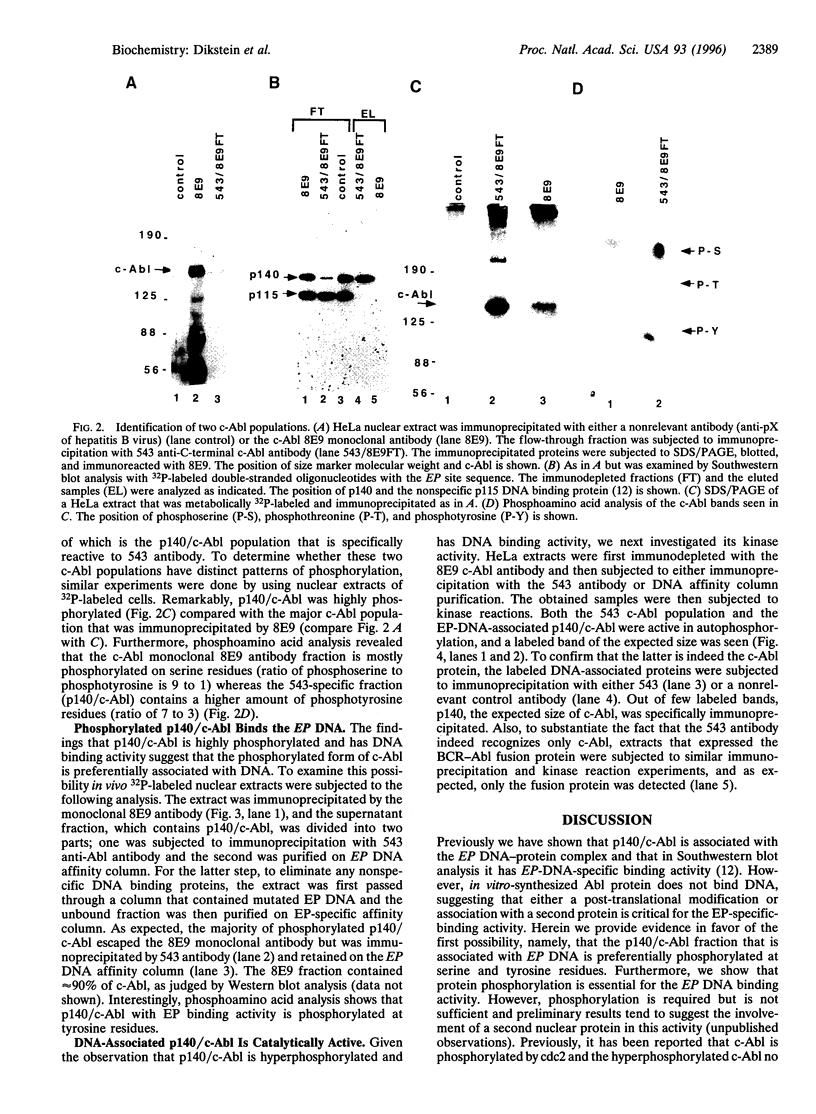
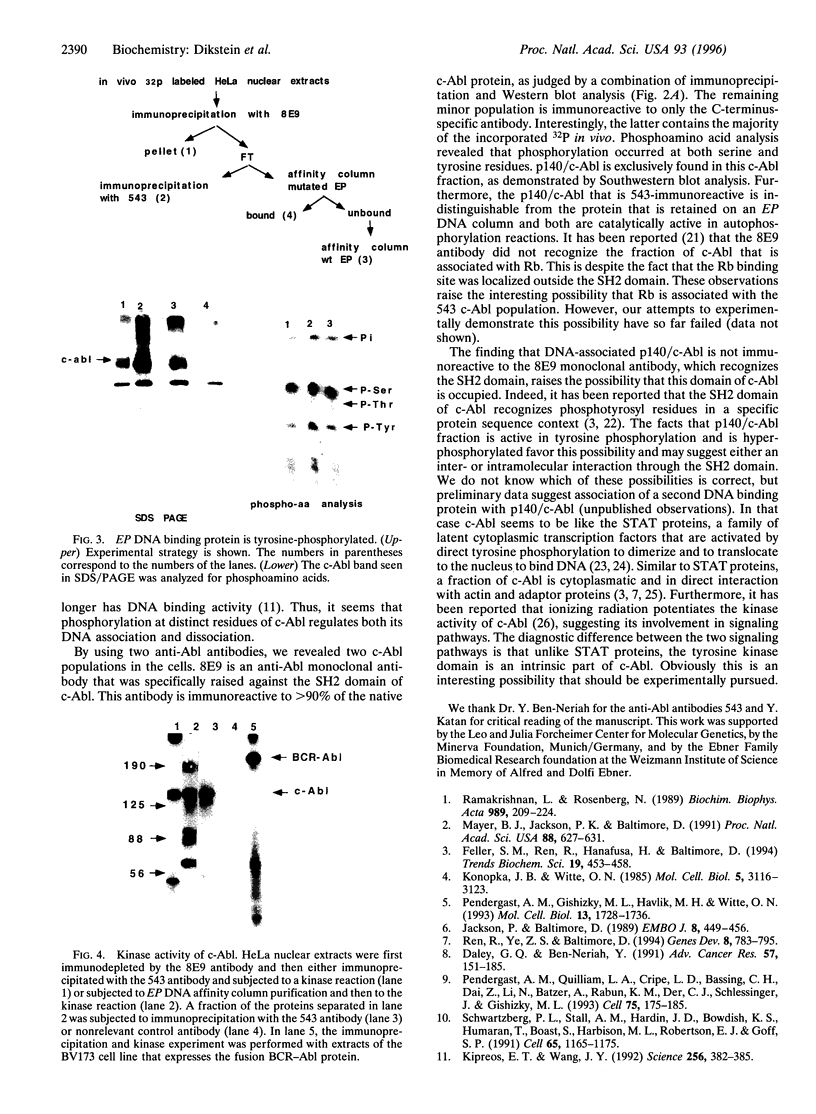
EP is a DNA element found in the enhancer and promoter regions of several cellular and viral genes. Previously, we have identified the DNA binding p140/c-Abl protein that specifically recognizes this element. Here we show that phosphorylation is essential for the p140/c-Abl DNA binding activity and for the formation of DNA-protein complexes. Furthermore, by 32P labeling of cells and protein purification, we demonstrate that in vivo the EP-DNA-associated p140/c-Abl is a tyrosine phosphoprotein. By employing two different c-Abl antibodies, we demonstrate the existence of two distinct c-Abl populations in cellular extracts. p140/c-Abl is quantitatively the minor population, is heavily phosphorylated at both serine and tyrosine residues, and is active in autophosphorylation reactions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anafi M., Gazit A., Gilon C., Ben-Neriah Y., Levitzki A. Selective interactions of transforming and normal abl proteins with ATP, tyrosine-copolymer substrates, and tyrphostins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4518–4523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley G. Q., Ben-Neriah Y. Implicating the bcr/abl gene in the pathogenesis of Philadelphia chromosome-positive human leukemia. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:151–184. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60998-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Faktor O., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. Functional organization of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3683–3689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Heffetz D., Ben-Neriah Y., Shaul Y. c-abl has a sequence-specific enhancer binding activity. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):751–757. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90287-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller S. M., Ren R., Hanafusa H., Baltimore D. SH2 and SH3 domains as molecular adhesives: the interactions of Crk and Abl. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):453–458. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller S. M., Wong T. W. Identification and characterization of a cytosolic protein tyrosine kinase of HeLa cells. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3044–3051. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Baltimore D. N-terminal mutations activate the leukemogenic potential of the myristoylated form of c-abl. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):449–456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Ren R., Pandey P., Shafman T. D., Feller S. M., Weichselbaum R. R., Kufe D. W. Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):785–788. doi: 10.1038/376785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipreos E. T., Wang J. Y. Cell cycle-regulated binding of c-Abl tyrosine kinase to DNA. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Witte O. N. Detection of c-abl tyrosine kinase activity in vitro permits direct comparison of normal and altered abl gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3116–3123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Baltimore D. The noncatalytic src homology region 2 segment of abl tyrosine kinase binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated cellular proteins with high affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):627–631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jackson P. K., Van Etten R. A., Baltimore D. Point mutations in the abl SH2 domain coordinately impair phosphotyrosine binding in vitro and transforming activity in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):609–618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhirter J. R., Wang J. Y. An actin-binding function contributes to transformation by the Bcr-Abl oncoprotein of Philadelphia chromosome-positive human leukemias. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1533–1546. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Scheirle G., Hearing P. Binding of nuclear factor EF-C to a functional domain of the hepatitis B virus enhancer region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2787–2797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Gishizky M. L., Havlik M. H., Witte O. N. SH1 domain autophosphorylation of P210 BCR/ABL is required for transformation but not growth factor independence. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1728–1736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Quilliam L. A., Cripe L. D., Bassing C. H., Dai Z., Li N., Batzer A., Rabun K. M., Der C. J., Schlessinger J. BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):175–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan L., Rosenberg N. abl genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 17;989(2):209–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Ye Z. S., Baltimore D. Abl protein-tyrosine kinase selects the Crk adapter as a substrate using SH3-binding sites. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):783–795. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P. L., Stall A. M., Hardin J. D., Bowdish K. S., Humaran T., Boast S., Harbison M. L., Robertson E. J., Goff S. P. Mice homozygous for the ablm1 mutation show poor viability and depletion of selected B and T cell populations. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1165–1175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90012-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Horvath C. M., Huang L. H., Qureshi S. A., Cowburn D., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon activation of the transcription factor Stat91 involves dimerization through SH2-phosphotyrosyl peptide interactions. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegrist C. A., Durand B., Emery P., David E., Hearing P., Mach B., Reith W. RFX1 is identical to enhancer factor C and functions as a transactivator of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6375–6384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch P. J., Wang J. Y. A C-terminal protein-binding domain in the retinoblastoma protein regulates nuclear c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the cell cycle. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90497-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., McLeod M. The sak1+ gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes an RFX family DNA-binding protein that positively regulates cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase-mediated exit from the mitotic cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1479–1488. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]