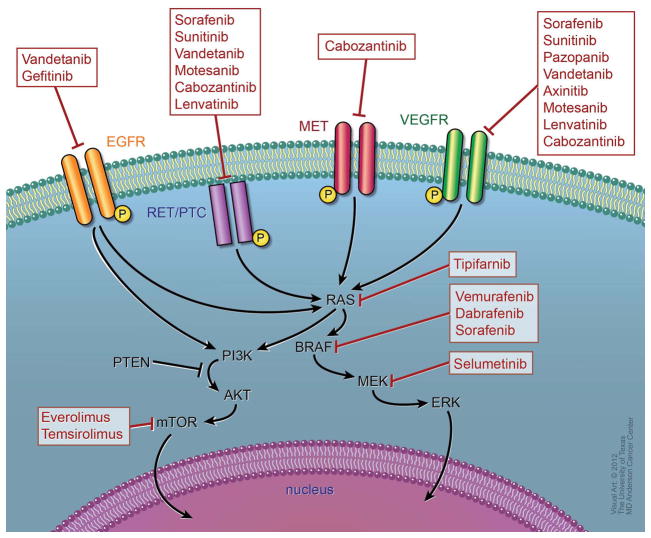
Figure 2.
Molecular signaling pathways and drug targets in DTC: The main signaling pathways in thyroid carcinogenesis are the Ras/Raf/MAPK and P13K-AKT pathways. Extracellular signals activate tyrosine kinase receptors leading to activation of Ras, which in turn activates Raf (mainly BRAF in DTC). Activated BRAF phosphorylates and activates the MEK, which in turn phosphorylates and activates ERK. Activated ERK translocates into the nucleus, where it regulates transcription of the genes involved in cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival. PI3K-Akt indirectly activates mTOR and it is a key regulator of cell proliferation and inhibitor of apoptosis. Signaling cascade is blocked with newer targeted therapies. The key targets that are currently under evaluation in phase II and III clinical trials in DTC are shown. *Although, no information is available to date, inhibitors of RET should theoretically inhibit RET/PTC similarly
Abbreviations: EGFR= epidermal growth factor receptor, VEGFR=vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, MAPK= mitogen-activated protein kinases; MEK= MAPK kinase; ERK= extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K=phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; mTOR= mammalian target of rapamycin.