Figure 3. Germ cell differentiation and maturation within the developing ovary.
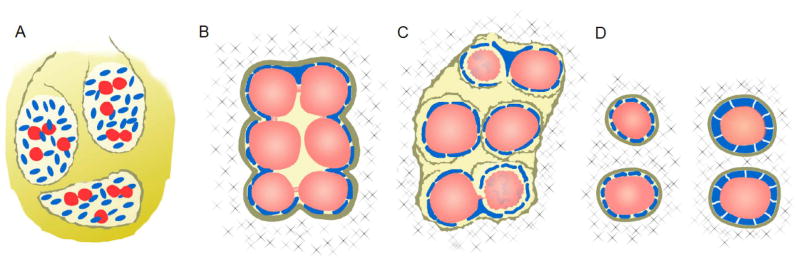
Germ cells undergo synchronous divisions and may aggregate with other dividing germ cells to form germ-line cysts. Thereafter, they differentiate into oocytes by initiating the first meiotic division. Around the time of birth, germ-line cysts break down, some oocytes die, and primordial follicles containing single oocytes form. (A) PGC arrival and organization into ovigerous cords (germ-line cysts) (E11.5-13.5): the basal lamina (brown lines) break down and then reform around proliferating somatic cells (blue cells) to surround invading PGCs (red cells) that aggregate and initiate synchronous divisions to form germ-line cysts. Synchronous division results in germ cell-germ cell syncytia with intercellular bridges. (B) Germ-line cysts coordinate oocyte specification (E13.5-17.5): each germ-line cyst includes clusters of germ cells that are completely surrounded by pre-granulosa cells (blue), a new basal lamina (brown line), and extracellular matrix (X). Several germ-line cysts grow within the developing ovary. Germ cells within the cyst begin to differentiate by initiating meiotic division (germ cell color changes from red to light coral) in response to retinoic acid signaling. Somatic cells remain intimately associated with oocytes and send projections deep into the syncytia. (C) Germ-line cyst breakdown initiates shortly before birth (E17.5-P2): Somatic cells begin to send long, invasive projections between oocytes, the basal lamina break down, and many oocytes die (wrinkled coral/blue germ cells) as germ-line cysts break down and follicles begin to form. The earliest follicles begin to form in the medulla as early as E17.5; the last follicles form at the cortex (P0-P2). (D) Primordial follicle formation and maturation to primary follicle (P0-P4): Interactions between the extracellular matrix (X), basal lamina (brown lines), somatic cells (blue), and oocytes (coral) facilitate organization into primordial follicles. Primordial follicles are characterized by squamous somatic cells (granulosa cells), which transition to a cuboidal shape upon maturation to primary follicles.
