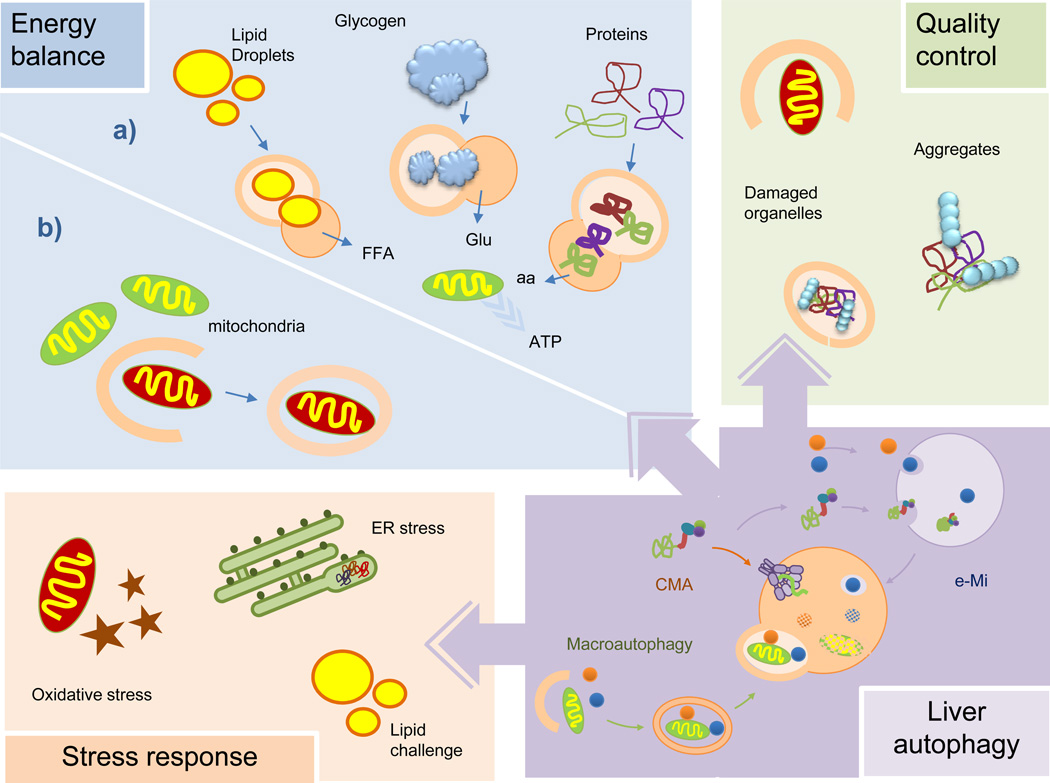
Figure 3. Functions of autophagy in liver physiology.
Autophagy maintains the energetic balance of the liver through turnover of different energy stores (a) and elimination of dysfunctional mitochondria (b). Autophagy eliminates altered proteins and organelles, as part of its function in cellular quality control, which otherwise will become toxic for hepatocytes. Liver autophagy is also activated for defense against hepatic damage resulting from oxidative stress, organelle stress (ER stress depicted here) or that induced by massive arrival of nutrients (lipotoxic challenge depicted here). aa: amino acids; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; FFA: free fatty acids; Glu: glucose.