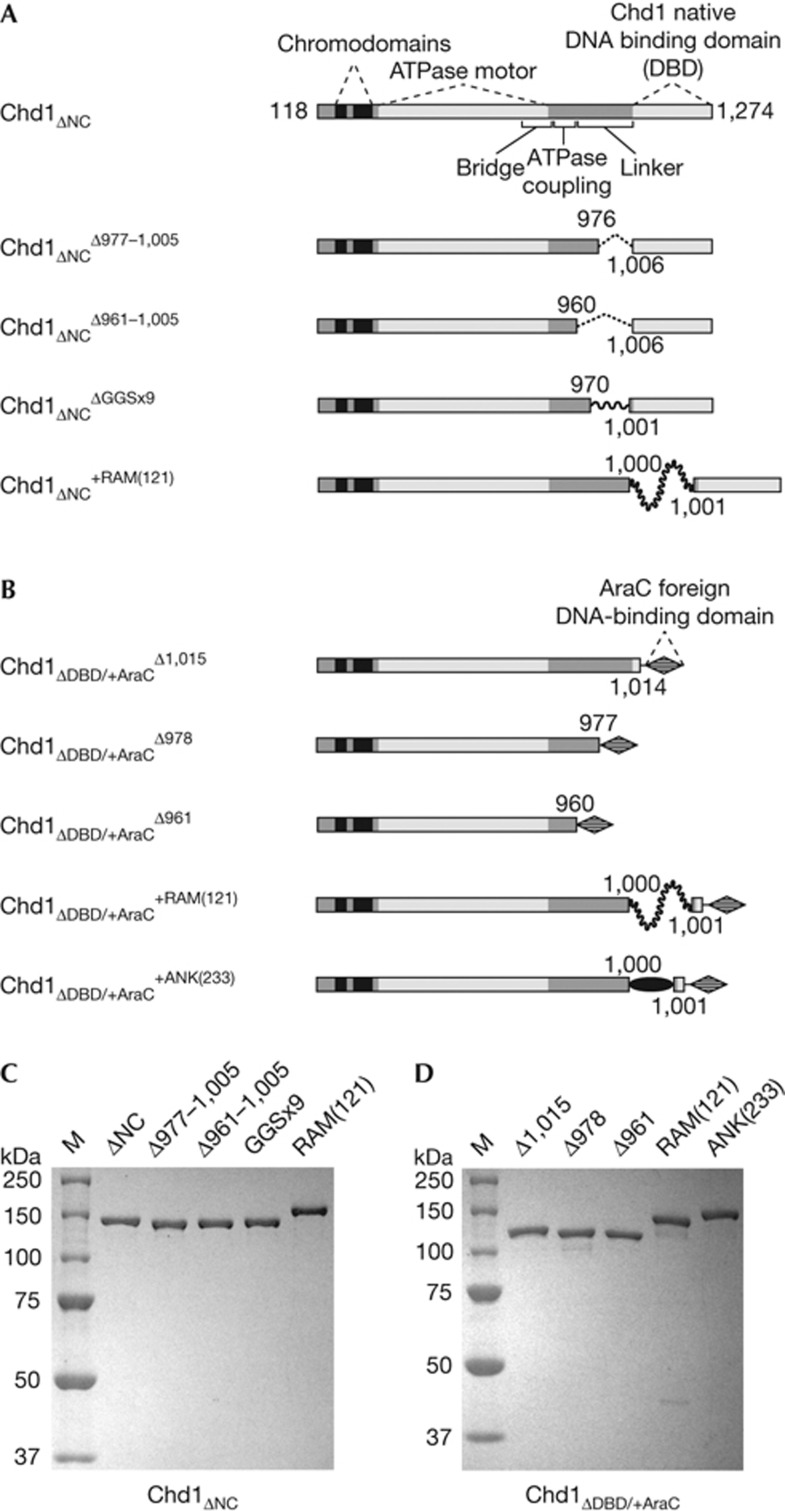
Figure 1.
Overview of S. cerevisiae Chd1 constructs used in this study. (A) Chd1 variants possessing the native Chd1 DBD. All constructs were on the basis of an N- and C-terminally truncated variant spanning residues 118–1,274, which includes the double chromodomains, ATPase motor and DBD, and are indicated with the subscript ΔNC. All changes to the DBD linker are denoted with superscripts, with the locations of the deletions, replacement and insertions labelled on the schematics. GGSx9 stands for nine Gly-Gly-Ser repeats, which replaced Chd1 residues 971–1,000. The +RAM(121) construct contains a 121-residue insertion of the RAM segment (residues 1,763 to 1,883) from the Drosophila melanogaster Notch receptor. (B) Chd1 variants possessing the foreign AraC DBD. All constructs contained the DBD of the AraC transcriptional regulator (residues 175–281) in place of the native Chd1 DBD, denoted with the subscript ΔDBD/+AraC. As in (A), superscripts refer to changes in the DBD linker, with Δ1,015, Δ978 and Δ961 referring to the beginning of the deletion replaced by the AraC DBD. The +ANK(233) construct contained the ankyrin domain (residues 1,907–2,139) of D. melanogaster Notch. Note that domains in A and B are not drawn to scale. (C) and (D) Purified proteins containing the native Chd1 DBD (C) or with the foreign AraC DBD (D) on SDS–PAGE gels stained with GelCode Blue. ANK, Ankyrin; DBD, DNA-binding domain; SDS–PAGE, SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis