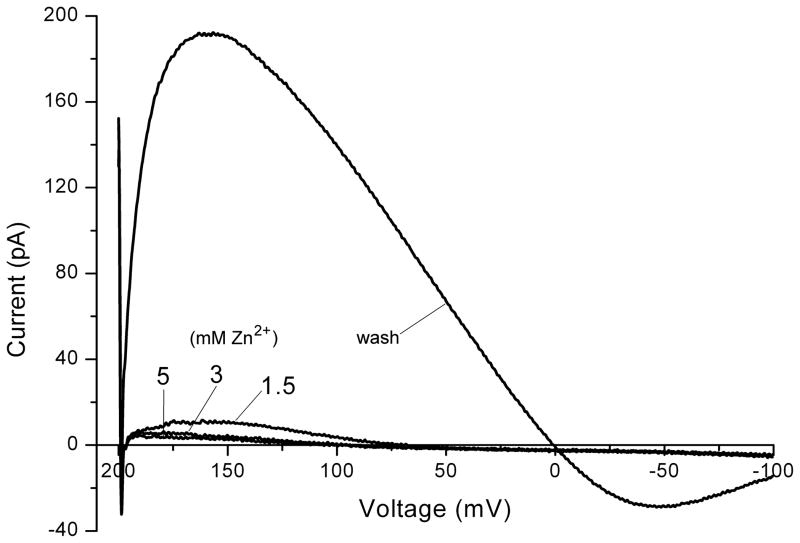
Fig. 6.
Evaluation of Vrev using voltage ramps. Currents during voltage ramps (from +200 mV to −100 mV in 800 ms) in a human eosinophil studied in perforated-patch configuration with KMeSO4 in the pipette solution and TMAMeSO4 in the bath solution, both at pH 7.0 and both with 50 mM NH4+ to clamp pHi near pHo. The predominant conductance is due to voltage-gated proton channels, which are inhibited by Zn2+. The sequence was 1.5 mM ZnCl2, then 5 mM, then 3 mM, then washout with EGTA-containing bath solution. This cell was stimulated with PMA and the DPI was added to inhibit NADPH oxidase.