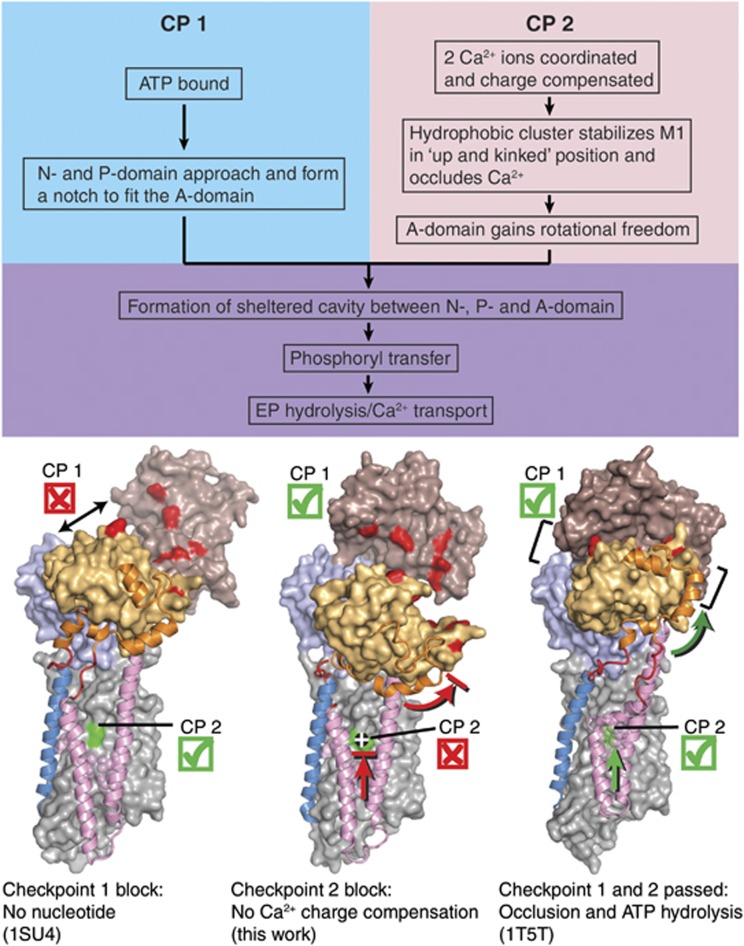
Figure 8.
Scheme for the structural requirements of SERCA for Ca2+-dependent activation of phosphorylation by ATP. The three structures shown are (from left to right): wild-type Ca2E1 (PDB 1SU4; Toyoshima et al. 2000), E309Q Ca2E1 (AMPPCP) (present work), and wild-type [Ca2]E1-AlF4−-ADP (PDB 1T5T; Sørensen et al, 2004). Requirements at both ‘checkpoints’, CP1 and CP2, have to be met; otherwise, the enzyme activity will be strongly lowered or completely abolished. In each structure, M1 and M2 are shown in pink cartoon, M3 in blue cartoon, the A-M1 and A-M3 linker regions in red cartoon, and the N-terminal part of the A-domain (amino acids 1–46) in orange cartoon, to aid in visualizing the upward motion of the M1/M2 bundle as well as the rotational motion of the A-domain upon nucleotide binding to the wild type. The remainder of the ATPase molecule is shown in surface representation, with the N-domain in brown, the P-domain in light blue, the A-domain in light orange, and the transmembrane domain in light grey. Some of the amino acids involved in interdomain contacts and Ca2+ binding are highlighted in the surface representation by red and green colouring, respectively.