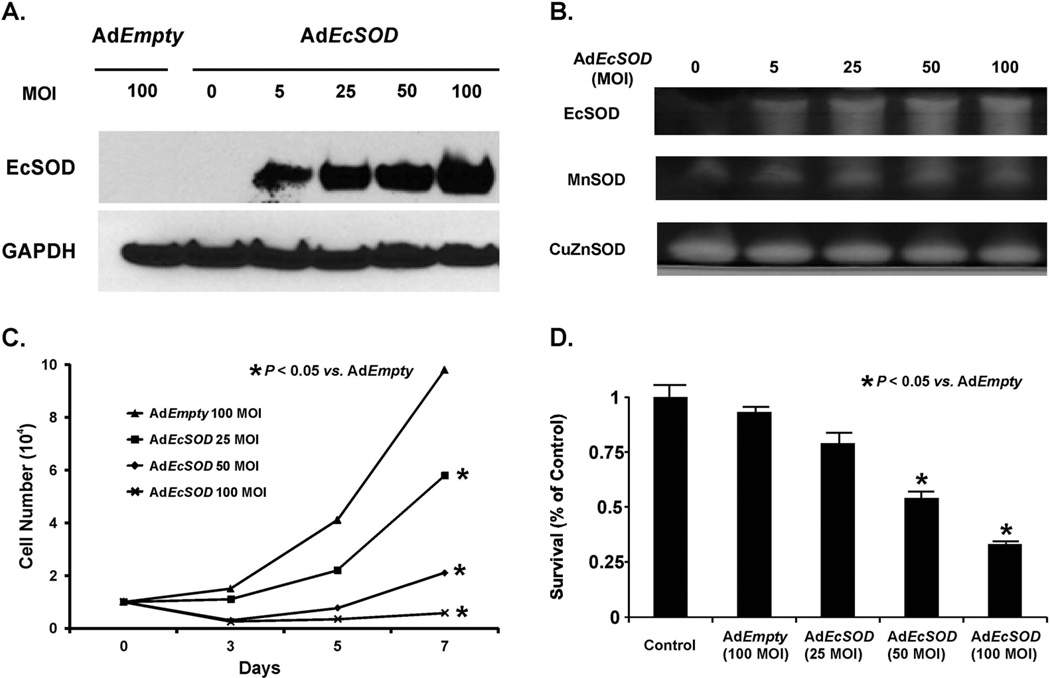
Figure 1. Adenoviral transduction of EcSOD inhibits hypoxic pancreatic cancer cell growth.
A. Western blot analysis demonstrates increases in EcSOD immunoreactivity of adenoviral infected MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells with increasing MOI. AdEmpty (100 MOI) as a negative control or AdEcSOD (0–100 MOI) was applied to cells for 24 h in 21% O2. Cells were exposed to 4% O2. Western blot demonstrates no detectable EcSOD immunoreactivity in the AdEmpty (100 MOI) or non-infected cells (0 MOI) but direct increases in EcSOD immunoreactivity with increasing MOI.
B. SOD enzymatic activities of adenoviral infected MIA PaCa-2 cells. Total cell lysate was assayed for SOD activities demonstrating increases in EcSOD activity with increasing viral titer but no changes in either the CuZnSOD or MnSOD activities.
C. AdEcSOD inhibited cell growth in 4% O2. MIA PaCa-2 cells were treated with AdEmpty (100 MOI) or AdEcSOD (25–100 MOI). Increasing viral titers of AdEcSOD inhibited cell growth. Each point represents the mean of three separate experiments. Mean ± SEM, n = 3. p < 0.05 vs. 100 MOI AdEmpty.
D. AdEcSOD inhibits clonogenic survival. MIA PaCa-2 cells were treated with AdEcSOD (25–100 MOI) and cultured for 14 days in 4% O2. Increasing viral titers decreased clonogenic survival with significant reductions at AdEcSOD 50 and 100 MOI compared to AdEmpty 100 MOI. Each point represents the mean of three separate experiments. Mean ± SEM, n = 3. p < 0.05 vs. 100 MOI AdEmpty.