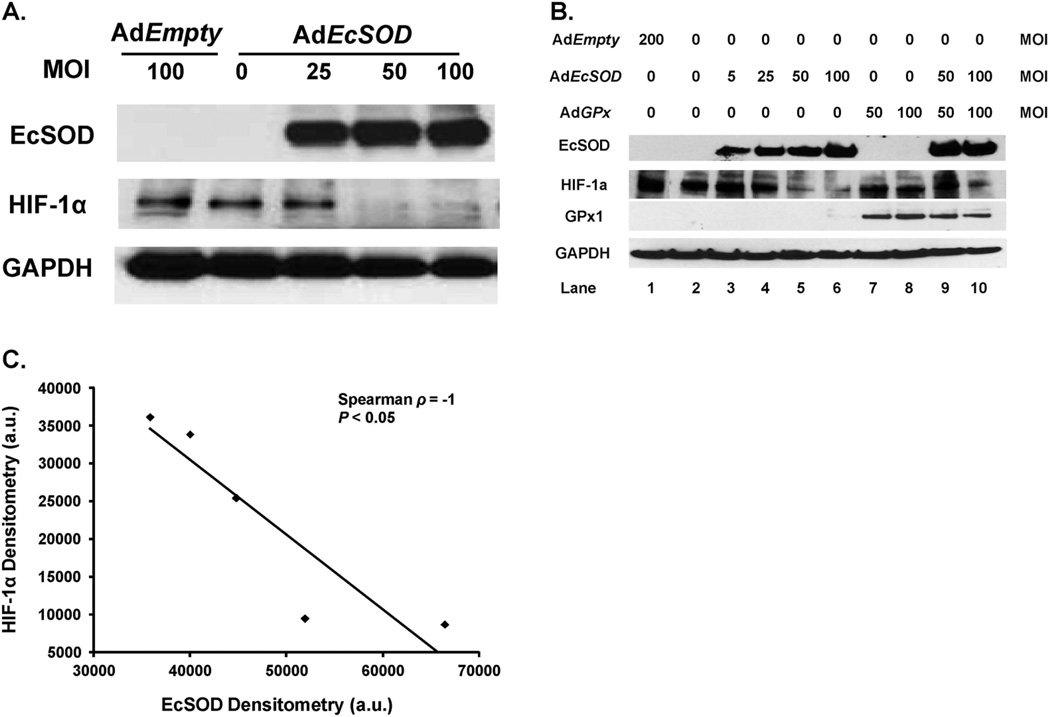
Figure 2. EcSOD modulates HIF-1α accumulation in pancreatic cancer cells.
A. Human pancreatic cancer cells were infected with the AdEcSOD or AdEmpty vectors and exposed to 4% O2. Protein was harvested for EcSOD and HIF-1α Western blot analysis. EcSOD inhibited HIF-1α accumulation in MIA PaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer cells.
B. EcSOD-induced decreases in HIF-1α protein accumulation were not reversed with GPx. Western analysis of MIA PaCa-2 cells infected with the AdEmpty, AdGPx, and AdEcSOD vectors or combinations. To equalize the viral load of the combined virus in these experiments, the AdEmpty vector was given. For example, the 50 MOI AdGPx was given along with 50 MOI AdEmpty to equal the viral load of the combination of AdGPx (50 MOI) + AdEcSOD (50 MOI). The EcSOD overexpression-induced inhibition of HIF-1α accumulation was not reversed with overexpression of GPx.
C. Inverse correlation between EcSOD immunoreactive protein and HIF-1α protein accumulation in MIA PaCa-2 cells. HIF-1α protein levels were quantified by densitometry using Image J analysis (V1.43i). Spearman correlation coefficient demonstrates a significant inverse relationship. Five points are shown here. Lanes 1, 3, 4, 5 and 6 from Figure 2B were used in the analysis.