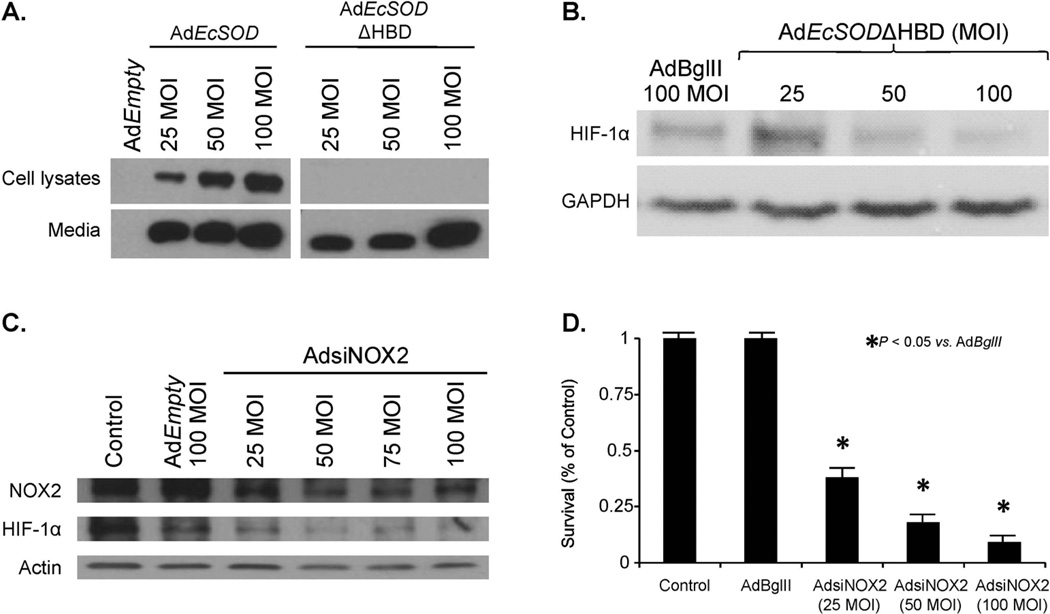
Figure 4. Non-mitochondrial superoxide alters HIF-1α protein accumulation.
A. MIA PaCa-2 cells were infected with the AdEmpty, AdEcSOD, or EcSOD with deletion of its heparin binding domain, AdEcSODΔHBD, and exposed to 4% O2. Western blot analysis once again demonstrated overexpression of EcSOD in cells treated with AdEcSOD. However, in cells treated with AdEcSODΔHBD there was an absence of cellular increases in EcSOD but EcSOD was increased in the media.
B. AdEcSODΔHBD inhibits HIF-1α accumulation. Cells were infected with the AdEcSOD, AdEcSODΔHBD or AdBglII vectors and exposed to 4% O2. Overexpression of EcSOD with AdEcSODΔHBD inhibited HIF-1α accumulation in MIA PaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer cells.
C. An adenoviral vector expressing siRNA against NOX2 (AdsiNOX2) was transfected into the MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cell line and grown in 4% oxygen. AdsiNOX2 (25–100 MOI) decreased immunoreactive protein when compared to both the parental cell line and cells transfected the adenoviral control vector AdEmpty (100 MOI). In addition to knockdown of NOX2, there was an inhibition of HIF-1α accumulation in cells treated with the AdsiNOX2 vector.
D. AdsiNOX2 infection (25–100 MOI) in MIA PaCa-2 cells decreased surviving fraction when compared to the same cell line infected with the AdBglII vector (100 MOI). Each point represents the mean values, with p < 0.05 vs. AdBglII, n = 3.