Fig. 2. Active and placebo acupuncture needles as well as the acupuncture points.
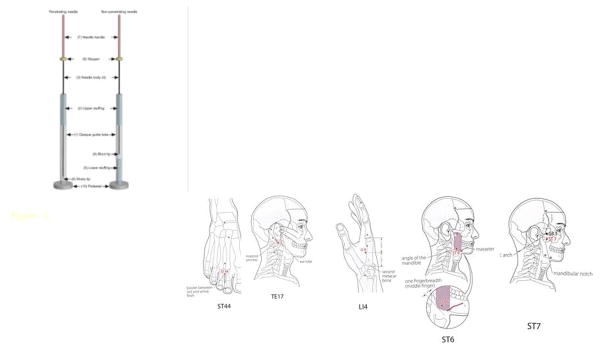
Each needle assembly comprises an opaque guide tube (1) and upper stuffing (2) to provide resistance to the needle body during its passage through the guide tube. The body of penetrating needle (3) is longer than the guide tube by an amount equal to the insertion depth, but the body of the non-penetrating needle (4) is only long enough to allow its blunt tip to press against the skin when the needle body is advanced to its limit. The non-penetrating needle contains stuffing at the bottom as well (5) to give a sensation similar to that of skin puncture and tissue penetration. Both needles have a stopper (6) that prevents the needle handle (7) from advancing further when the sharp tip of the penetrating needle (8) or the blunt tip of the non-penetrating needle (9) reaches the specified position. The pedestal (10) on each needle is adhesive, allowing it to adhere firmly to the skin surface. The diameter of the needles used in this study was 0.16 mm.
