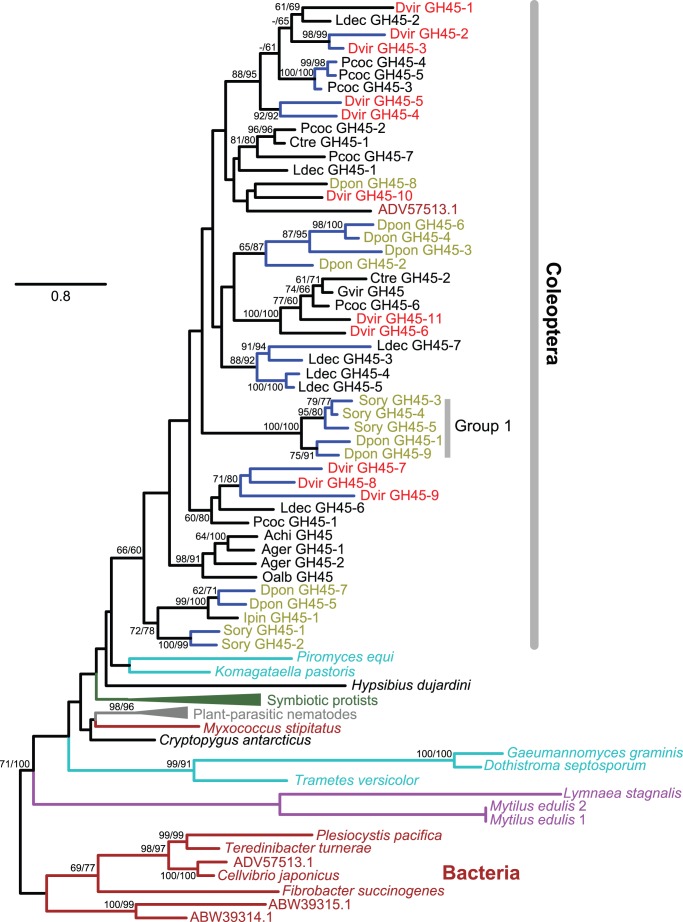
Figure 2. The maximum-likelihood phylogeny of GH45 proteins.
Forty seven GH45 protein sequences from eleven coleopteran species are included. Their species name abbreviations are found in Table S5. Labels for the coleopteran species belonging to the superfamily Curculionoidea are olive-colored and all other coleopteran sequences colored in black belong to the superfamily Chrysomeloidea. D. v. virgifera sequences are shown in red. Other sequences include: two mollusks (purple), Cryptopygus antarcticus (Collembola, black), Hypsibius dujardini (Tardigrada, black), 24 termite-symbiotic protists (dark green), 10 plant-parasitic nematodes (all are from Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, grey), representative fungi (chosen from 138 sequences, cyan), and representative bacteria (chosen from 18 sequences, brown). Bacterial sequences were used as outgroups. The numbers at internal branches show the bootstrap support values (%) for the maximum-likelihood and neighbor-joining phylogenies in this order. Supporting values are shown only when higher than 60%. Blue-colored branches indicate the species-specific gene duplications (based on currently available sequences) within a cluster supported by higher than 70% of bootstrap values. The scale bar represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. See Figure S2 for more details.