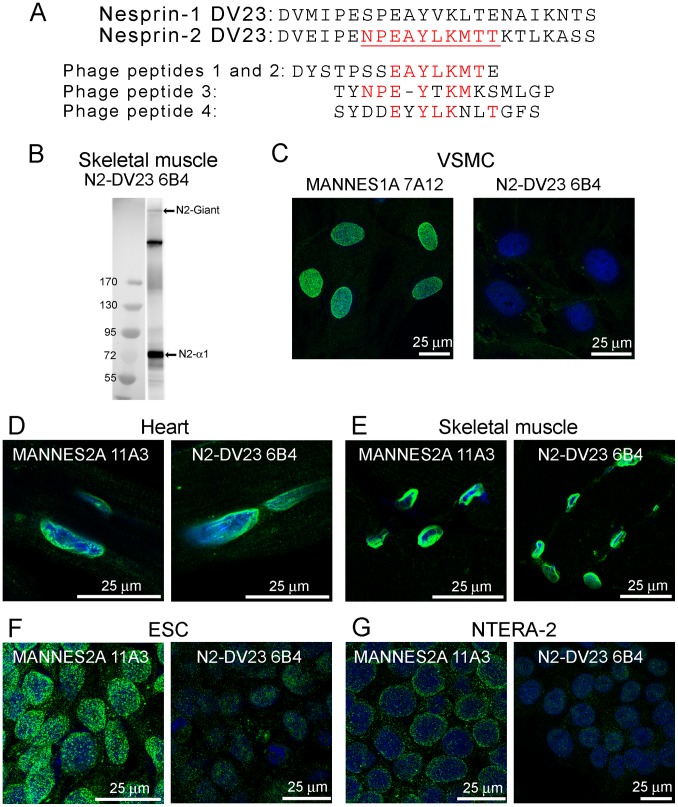
Figure 8. Immunolocalisation of isoforms lacking the DV23 region and/or the KASH domain.
(A) Alignment of the 23 amino acid sequences of the DV23 exon of nesprin-1 and nesprin-2. The nesprin-2 DV23 peptide was the immunogen for mAb production. The epitope of the mAbs was mapped to the sequence shown in red and underlined. Sequences of the four 15-mer peptides pulled out of the phage-display peptide library are shown aligned below the nesprin-2 DV23 sequence, with matching amino acids shown in red. (B) The mAb N2-DV23 6B4 recognised bands of nesprin-2-giant and nesprin-2-alpha-1 in western blot of skeletal muscle (the intermediate band is a likely degradation product of nesprin-2-giant). (C) The 6B4 mAb against nesprin-2 DV23 does not cross-react with nesprin-1 DV23. VSMC (which contain nesprin-1 with DV23 but no nesprin-2) showed nuclear staining for nesprin-1 with MANNES1A but not with 6B4. Immunofluorescent staining with mAbs MANNES2A and N2-DV23 6B4 was equally strong on both cardiac muscle nuclear rim (D) and skeletal muscle nuclear rim (E). However, MANNES2A was much stronger than N2-DV23 6B4 on both ESC (F) and Ntera-2 cells (G), since the DV23 exon is mainly excluded in these cells (see Fig. 7B). Furthermore, the MANNES1A mAb is largely nucleoplasmic in ESC, which may be because the nesprin-2 KASH domain is also largely excluded in this cell type (see Fig. 7D).