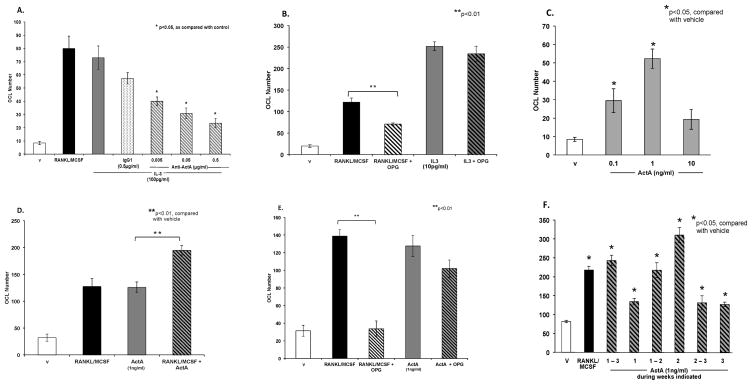
Figure 1.
Figure 1A: Anti-Activin A decreases IL-3 induced osteoclastogenesis. Human non-adherent BM cells (OCL precursors) were cultured in the presence of vehicle, rhRANKL (50ng/ml) with rhMCSF (10ng/ml), IL-3 (100pg/ml) , IL-3 with IgG1 isotype control (0.5μg/ml), and varying concentrations of a neutralizing antibody to ActA (anti-ActA) in combination with IL-3. Following 21days of culture, cells were fixed and stained. 23c6+ multinucleated cells were counted. The osteoclastogenic effects of IL-3 were significantly inhibited by anti-ActA in a dose-dependent manner.
Figure 1B: IL-3 induced osteoclastogenesis is RANKL independent. OCL precursors were cultured in the presence of RANKL/MCSF or IL-3 (10pg/ml) in the presence or absence of osteoprotegerin (OPG), a decoy receptor for RANKL. OPG completely inhibited RANKL induced OCL formation, as expected. However, OPG only slightly decreased IL-3 induced OCL formation, demonstrating that IL-3 induced osteoclastogenesis occurs via a RANKL-independent mechanism.
Figure 1C: ActA increases OCL number. OCL precursors were cultured in the presence of varying doses of ActA for 21 days. At the end of the culture period cells were fixed and stained for α5β3 integrin with 23c6+ antibody. 23c6+ multinucleated cells were quantified. ActA enhances osteoclastogenesis significantly at doses of 0.1 and 1 ng/ml.
Figure 1D: RANKL enhances ActA induced osteoclastogenesis. OCL precursors were cultured in RANKL/MCSF, ActA alone (1ng/ml), or both for 21 days. At the conclusion of the culture period, cells were fixed and stained. 23c6+ cells were counted. ActA induced osteoclastogenesis was significantly increased in the presence of RANKL/MCSF.
Figure 1E: ActA induced osteoclastogenesis is also RANKL independent. OCL precursors were cultured in the presence of RANKL/MCSF or ActA in the presence or absence of OPG. OPG alone modestly reduced ActA induced OCL formation, demonstrating that ActA induced osteoclastogenesis, like IL-3 induced osteoclastogenesis, is RANKL-independent.
Figure 1F: Activin A acts early in osteoclastogenesis. OCL precursors were cultured in the presence of ActA during specified weeks of culture, then fixed and stained for 23c6+. While all cultures treated with ActA had significantly greater numbers of OCL than control culture (RANKL/MCSF), the most pronounced effect occurred during the first two weeks of culture.