Abstract
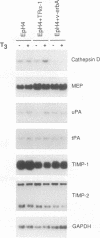
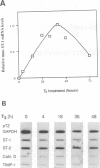
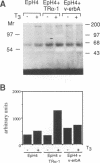
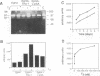
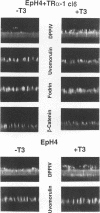
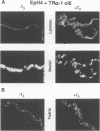
Stromelysins are a group of proteases which degrade the extracellular matrix and activate other secreted proteases. Stromelysin (ST)-1 and ST-2 genes are induced by tumor promoters, oncogenes and growth factors, and have been involved in acquisition of the malignant phenotype. We show here that the thyroid hormone (T3) increases ST-1 and ST-2 expression in a non-transformed mouse mammary epithelial cell line (EpH4) in a way that is dependent on the level of thyroid receptor/c-erbA (TR alpha-1) expression. In agreement with this, T3 increases the secreted stromelysin activity and enhances the gelatinolytic activity of type IV collagenase. We have also demonstrated that T3 affects the epithelial polarity of EpH4 cells, diminishing the transepithelial electrical resistance of monolayers cultured on permeable filters, causing an abnormal distribution of polarization markers and the disruption of the organized 3-D structures formed by these cells in type I collagen gels. These results indicate that the ligand-activated TR alpha-1 plays an important role in regulating the morphogenetic and invasive capacities of mammary epithelial cells. Because the c-erbA locus is altered in several types of carcinoma, an altered or deregulated TR alpha-1 expression may also be important for breast cancer development and metastasis.
Full text
PDF
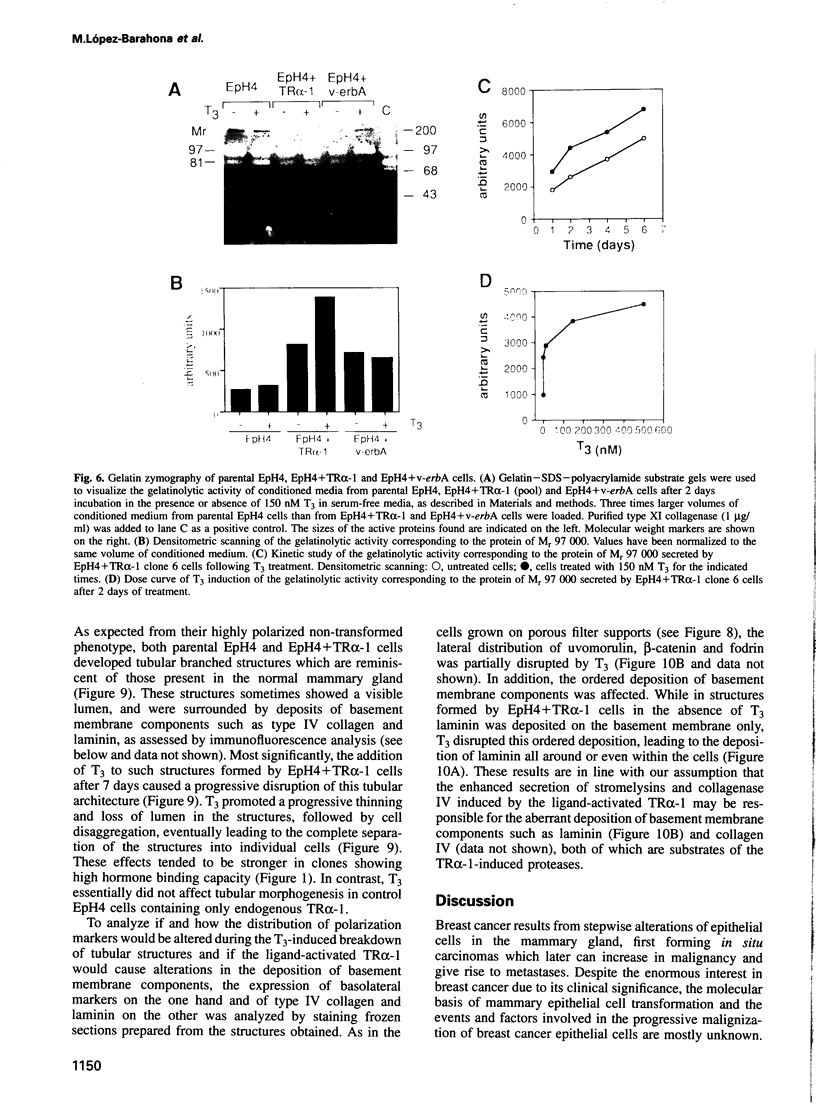
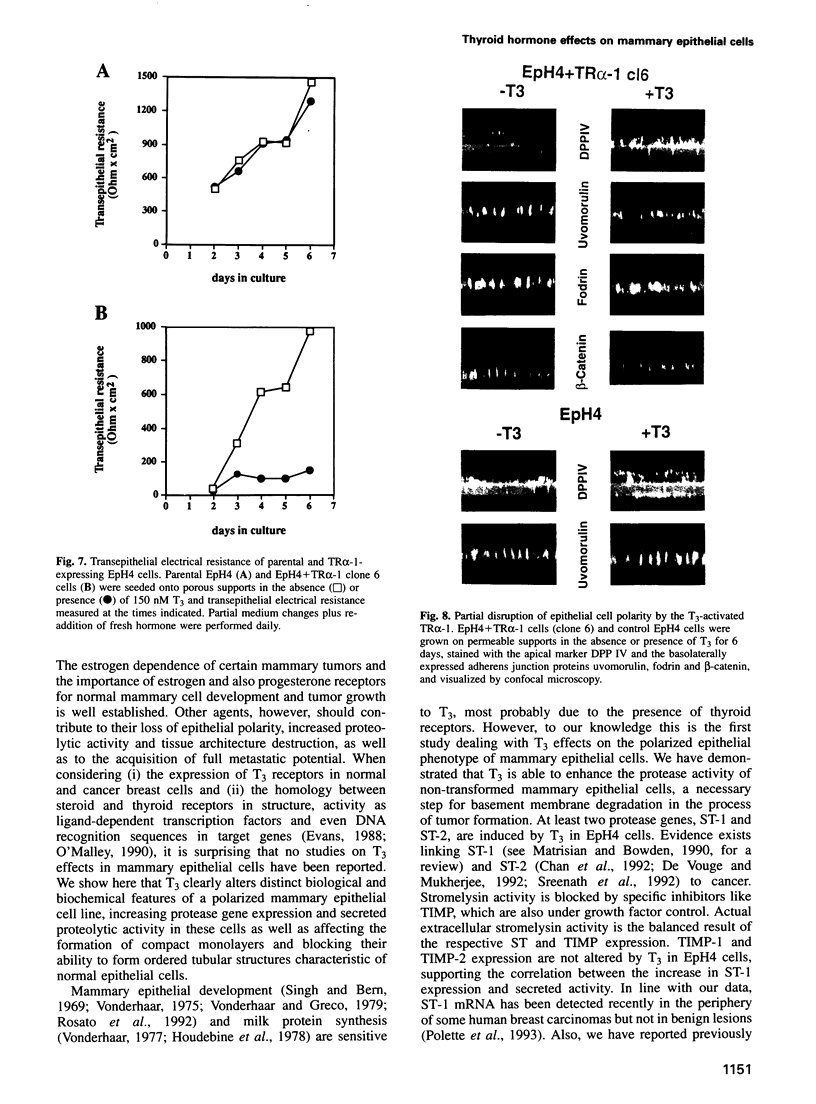

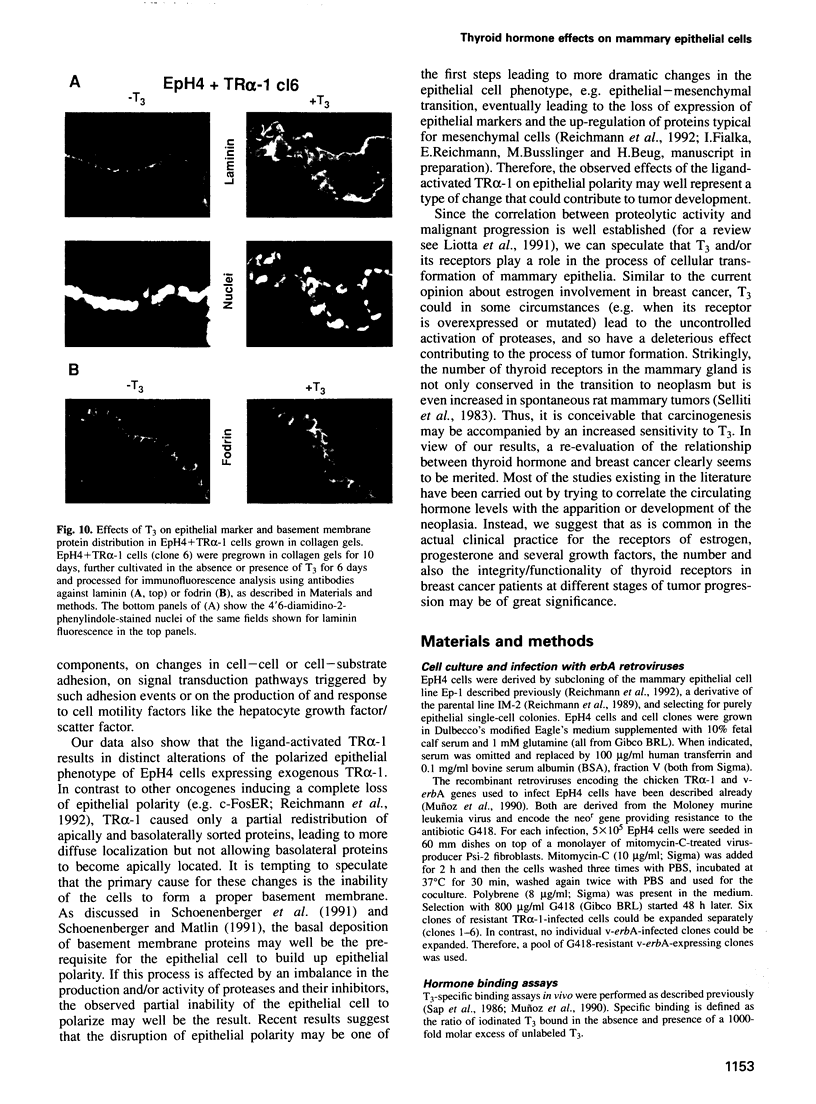


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Lidereau R., Callahan R. Presence of two members of c-erbA receptor gene family (c-erbA beta and c-erbA2) in smallest region of somatic homozygosity on chromosome 3p21-p25 in human breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Dec 6;81(23):1815–1820. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.23.1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnot P., Kew M., Parker I., Fitschen W. Expression of c-erbA in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1989 Jul-Aug;9(4):885–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Guernsey D. L., Fisher P. B. Regulation of anchorage-independent growth by thyroid hormone in type 5 adenovirus-transformed rat embryo cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Dec;45(12 Pt 1):6017–6023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballin M., Gomez D. E., Sinha C. C., Thorgeirsson U. P. Ras oncogene mediated induction of a 92 kDa metalloproteinase; strong correlation with the malignant phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):832–838. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstraesser L. M., Weitzman S. A. Culture of normal and malignant primary human mammary epithelial cells in a physiological manner simulates in vivo growth patterns and allows discrimination of cell type. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 1;53(11):2644–2654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard E. J., Muschel R. J., Hughes E. N. Mr 92,000 gelatinase release correlates with the metastatic phenotype in transformed rat embryo cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 1;50(13):3872–3877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borek C., Guernsey D. L., Ong A., Edelman I. S. Critical role played by thyroid hormone in induction of neoplastic transformation by chemical carcinogens in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5749–5752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Matrisian L. M., Gesnel M. C., Staub A., Leroy P. Sequences coding for part of oncogene-induced transin are highly conserved in a related rat gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1139–1151. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. D., Bloxidge R. E., Anderson E., Howell A. Expression of activated gelatinase in human invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1993 Mar;11(2):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00114976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., McGuire W. L. Nuclear thyroid hormone receptors in a human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3769–3773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnac G., Albagli-Curiel O., Desclozeaux M., Vandromme M., Glineur C., Bègue A., Laudet V., Bonnieu A. Overexpression of c-erbA proto-oncogene enhances myogenic differentiation. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):3103–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerbon M. A., Pichon M. F., Milgrom E. Thyroid hormone receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1981 Oct;41(10):4167–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. C., Scanlon M., Zhang H. Z., Jia L. B., Yu D. H., Hung M. C., French M., Eastman E. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of v-mos-activated transformation-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1099–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza B., Berdichevsky F., Kyprianou N., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Collagen-induced morphogenesis and expression of the alpha 2-integrin subunit is inhibited in c-erbB2-transfected human mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1797–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Selden J. R., Laws G., Dorney D. J., Finan J., Tripputi P., Emanuel B. S., Rovera G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. A human c-erbA oncogene homologue is closely proximal to the chromosome 17 breakpoint in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vouge M. W., Mukherjee B. B. Transformation of normal rat kidney cells by v-K-ras enhances expression of transin 2 and an S-100-related calcium-binding protein. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):109–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrovic A., Houle B., Belouchi A., Bradley W. E. erbA-related sequence coding for DNA-binding hormone receptor localized to chromosome 3p21-3p25 and deleted in small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 1;48(3):682–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabkin H., Kao F. T., Hartz J., Hart I., Gazdar A., Weinberger C., Evans R., Gerber M. Localization of human ERBA2 to the 3p22----3p24.1 region of chromosome 3 and variable deletion in small cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9258–9262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eil C., Douglass E. C., Rosenburg S. M., Kano-Sueoka T. Receptor characteristics of the rat mammary carcinoma cell line 64-24. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):42–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel G., Popowicz P., Marshall H., Norling G., Svensson C., Auer G., Akusjärvi G., Linder S. Elevated stromelysin-1 and reduced collagenase-IV expression in invasive rat embryo fibroblasts expressing E1A deletion mutants + T24-H-ras. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jul 9;51(5):761–766. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Guernsey D. L., Weinstein I. B., Edelman I. S. Modulation of adenovirus transformation by thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):196–200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futreal P. A., Söderkvist P., Marks J. R., Iglehart J. D., Cochran C., Barrett J. C., Wiseman R. W. Detection of frequent allelic loss on proximal chromosome 17q in sporadic breast carcinoma using microsatellite length polymorphisms. Cancer Res. 1992 May 1;52(9):2624–2627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M., Derocq D., Pujol P., Rochefort H. Overexpression of transfected cathepsin D in transformed cells increases their malignant phenotype and metastatic potency. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1809–1814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. B., Monson R. R., Maloof F. Benign thyroid diseases and the risk of death from breast cancer. Oncology. 1992;49(6):461–466. doi: 10.1159/000227093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. B. Thyroid diseases and breast cancer. Epidemiol Rev. 1990;12:16–28. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guernsey D. L., Borek C., Edelman I. S. Crucial role of thyroid hormone in x-ray-induced neoplastic transformation in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5708–5711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guernsey D. L., Ong A., Borek C. Thyroid hormone modulation of X ray-induced in vitro neoplastic transformation. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):591–592. doi: 10.1038/288591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden T. J., Forsyth I. A. Thyroid hormone binding in rat mammary gland [proceedings]. J Endocrinol. 1977 Dec;75(3):38P–39P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdebine L. M., Delouis C., Devinoy E. Post-transcriptional stimulation of casein synthesis by thyroid hormone. Biochimie. 1978;60(8):809–812. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Holt J. T., Matrisian L. M. Growth factors regulate transin gene expression by c-fos-dependent and c-fos-independent pathways. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.2462278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Miller D. B., Matrisian L. M. TGF-beta 1 inhibition of transin/stromelysin gene expression is mediated through a Fos binding sequence. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90807-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knabbe C., Lippman M. E., Wakefield L. M., Flanders K. C., Kasid A., Derynck R., Dickson R. B. Evidence that transforming growth factor-beta is a hormonally regulated negative growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P., Finch J., Füstenberger G., Melber K., Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T. Tumor promoters induce a transient expression of tumor-associated genes in both basal and differentiated cells of the mouse epidermis. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jan;9(1):95–100. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc F., Brauch H., Hajj C., Dobrovic A., Kaye F., Gazdar A., Harbour J. W., Pettengill O. S., Sorenson G. D., van den Berg A. Loss of heterozygosity in a gene coding for a thyroid hormone receptor in lung cancers. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;44(2):282–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C. A., Hsiao W. L., Weinstein I. B. Effects of triiodothyronine and tamoxifen on cell transformation induced by an activated c-Ha-ras oncogene. Cancer Res. 1989 Feb 15;49(4):895–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida C. M., Muldoon L. L., Rodland K. D., Magun B. E. Transcriptional modulation of transin gene expression by epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2479–2483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marguet D., Bernard A. M., Vivier I., Darmoul D., Naquet P., Pierres M. cDNA cloning for mouse thymocyte-activating molecule. A multifunctional ecto-dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26) included in a subgroup of serine proteases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2200–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Haut M., Stellato T., Gerbic C., Molkentin K. Expression of the ErbA-beta class of thyroid hormone receptors is selectively lost in human colon carcinoma. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1683–1687. doi: 10.1172/JCI114349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall E. Epidemiology. Search for a killer: focus shifts from fat to hormones. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):618–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8430308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T., Krieg P., Fürstenberger G., Briand J. P., Leroy P., Breathnach R. The mRNA coding for the secreted protease transin is expressed more abundantly in malignant than in benign tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9413–9417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T. Stromelysin/transin and tumor progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Apr;1(2):107–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Glaichenhaus N., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor and oncogenes induce transcription of the same cellular mRNA in rat fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Leroy P., Ruhlmann C., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Isolation of the oncogene and epidermal growth factor-induced transin gene: complex control in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz A., Höppner W., Sap J., Brady G., Nordström K., Seitz H. J., Vennström B. The chicken c-erbA alpha-product induces expression of thyroid hormone-responsive genes in 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptor-deficient rat hepatoma cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):312–320. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima M., Welch D. R., Belloni P. N., Nicolson G. L. Degradation of basement membrane type IV collagen and lung subendothelial matrix by rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell clones of differing metastatic potentials. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4869–4876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R. C., Mader S., Nagpal S., Leid M., Rochette-Egly C., Chambon P. Negative regulation of the rat stromelysin gene promoter by retinoic acid is mediated by an AP1 binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4443–4454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for the future. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):363–369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski L. E., Finch J., Krieg P., Matrisian L., Patskan G., O'Connell J. F., Phillips J., Slaga T. J., Breathnach R., Bowden G. T. Expression pattern of a gene for a secreted metalloproteinase during late stages of tumor progression. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(1):13–19. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. W., Rønnov-Jessen L., Howlett A. R., Bissell M. J. Interaction with basement membrane serves to rapidly distinguish growth and differentiation pattern of normal and malignant human breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9064–9068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M. Nuclear receptor/AP-1 interaction. Endocr Rev. 1993 Oct;14(5):651–658. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-5-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polette M., Clavel C., Cockett M., Girod de Bentzmann S., Murphy G., Birembaut P. Detection and localization of mRNAs encoding matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitor in human breast pathology. Invasion Metastasis. 1993;13(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichmann E., Ball R., Groner B., Friis R. R. New mammary epithelial and fibroblastic cell clones in coculture form structures competent to differentiate functionally. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):1127–1138. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichmann E., Schwarz H., Deiner E. M., Leitner I., Eilers M., Berger J., Busslinger M., Beug H. Activation of an inducible c-FosER fusion protein causes loss of epithelial polarity and triggers epithelial-fibroblastoid cell conversion. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1103–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochefort H., Capony F., Garcia M. Cathepsin D: a protease involved in breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Dec;9(4):321–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00049522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosato R. R., Gimenez M. S., Jahn G. A. Effects of chronic thyroid hormone administration on pregnancy, lactogenesis and lactation in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1992 Dec;127(6):547–554. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1270547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka F. J., Rose D. P. Nuclear thyroid hormone receptors, alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenases, and malic enzyme in N-nitrosomethylurea-induced rat mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3150–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Kida Y., Mai M., Endo Y., Sasaki T., Tanaka J., Seiki M. Expression of genes encoding type IV collagen-degrading metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in various human tumor cells. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenenberger C. A., Matlin K. S. Cell polarity and epithelial oncogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;1(4):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenenberger C. A., Zuk A., Kendall D., Matlin K. S. Multilayering and loss of apical polarity in MDCK cells transformed with viral K-ras. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):873–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellitti D. F., Tseng Y. C., Latham K. R. Nuclear thyroid hormone receptors in C3H/HeN mouse mammary glands and spontaneous tumors. Cancer Res. 1983 Mar;43(3):1030–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif M., Privalsky M. L. V-erbA and c-erbA proteins enhance transcriptional activation by c-jun. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):953–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh D. V., Bern H. A. Interaction between prolactin and thyroxine in mouse mammary gland lobulo-alveolar development in vitro. J Endocrinol. 1969 Dec;45(4):579–583. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0450579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreenath T., Matrisian L. M., Stetler-Stevenson W., Gattoni-Celli S., Pozzatti R. O. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase genes in transformed rat cell lines of high and low metastatic potential. Cancer Res. 1992 Sep 15;52(18):4942–4947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sympson C. J., Talhouk R. S., Alexander C. M., Chin J. R., Clift S. M., Bissell M. J., Werb Z. Targeted expression of stromelysin-1 in mammary gland provides evidence for a role of proteinases in branching morphogenesis and the requirement for an intact basement membrane for tissue-specific gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):681–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderhaar B. K. A role of thyroid hormones in differentiation of mouse mammary gland in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1219–1225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90803-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderhaar B. K., Greco A. E. Lobulo-alveolar development of mouse mammary glands is regulated by thyroid hormones. Endocrinology. 1979 Feb;104(2):409–418. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-2-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderhaar B. K. Studies on the mechanism by which thyroid hormones enhance alpha-lactalbumin activity in explants from mouse mammary glands. Endocrinology. 1977 May;100(5):1423–1431. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-5-1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorherr H. Thyroid function in benign and malignant breast disease. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Mar;23(3):255–257. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Brown D. D. Thyroid hormone-induced gene expression program for amphibian tail resorption. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16270–16278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Gorewit R. C. Specific thyroxine receptors in mammary cytosol from lactating cattle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 31;95(2):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90859-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Miyajima N., Toyoshima K., Nomura N., Sakamoto H., Yoshida T., Terada M., Sugimura T. Genetic alterations of the c-erbB-2 oncogene occur frequently in tubular adenocarcinoma of the stomach and are often accompanied by amplification of the v-erbA homologue. Oncogene. 1988 Mar;2(3):283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurzolo C., Le Bivic A., Quaroni A., Nitsch L., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Modulation of transcytotic and direct targeting pathways in a polarized thyroid cell line. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2337–2344. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]